|
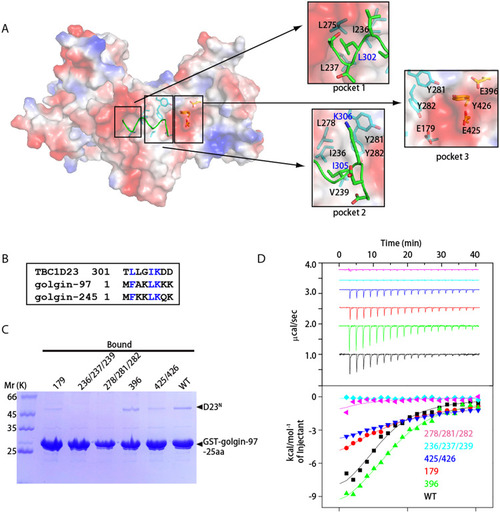
Both TBC and rhodanese domains of TBC1D23 interact with golgin-97/245.(A) Surface representation of one D23N monomer (molecule 1), with a fragment from symmetry-related D23N molecule shown as sticks (molecule 2, green). Molecule 1 is shown in the identical orientation to that in Fig 1B. Critical residues involved in dimerization are highlighted on the right, with residues from molecule 1 and 2 labeled in black and blue fonts, respectively. (B) Sequence alignment between residues from D23N-linker, N-terminus of golgin-97 and of golgin-245. Blue color indicates same or similar type of aa. (C) GST pull-down assays performed with GST-golgin-97-25aa and purified D23N WT, E179K (“179”), L278A/Y281A/Y282A (“278/281/282”), I236A/I237A/V239A (“236/237/239”), E396K (“396”), or E425K/Y426A (“425/426”). After incubation with soluble protein(s), the resin was extensively washed. The resin-bound proteins were then subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. (D) ITC experiments for the binding of golgin-97-25aa peptide with D23N WT, E179K (“179”), L278A/Y281A/Y282A (“278/281/282”), I236A/I237A/V239A (“236/237/239”), E396K (“396”), or E425K/Y426A (“425/426”). Top and bottom panels show raw and integrated heat from injections, respectively. The solid curves in the bottom panel represent a fit of the integrated data to a single-site binding model. Experiments were triplicated, and the numerical data are included in S1 Data. aa, amino acid; D23N, N-terminus of TBC1D23; GST, glutathione S-transferase; ITC, isothermal titration calorimetry; TBC, Tre2-Bub2-Cdc16; WT, wild type.
|