Figure 1 - figure supplement 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-200530-51
- Publication
- Kantarci et al., 2020 - The Warburg Effect and lactate signaling augment Fgf-MAPK to promote sensory-neural development in the otic vesicle
- Other Figures
-
- Figure 1
- Figure 1 - figure supplement 1
- Figure 2
- Figure 3
- Figure 3 - figure supplement 3
- Figure 3 - figure supplement 4
- Figure 3 - figure supplement 5
- Figure 4
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 1
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 2
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 3
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 4
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 5
- Figure 4 - figure supplement 6
- Figure 5
- Figure 6
- Figure 6 - figure supplement 1
- Figure 7
- text only
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
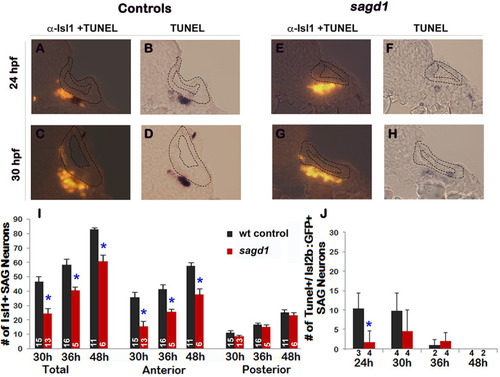
Quantitation of mature Isl1/2+ SAG neurons and TUNEL in sagd1 mutants.(A–H) Cross sections (dorsal up, medial to the right) through the anterior/vestibular portion of the otic vesicle in control embryos (A–D) and sagd1 mutants (E–H) showing anti-Isl1/2 stained SAG neurons (A,C, E, G) and co-staining for TUNEL (B, D, F, H). (I) Number of Isl1/2+ SAG neurons at 30 hpf counted from whole mount preparations. Anterior/vestibular SAG neurons are under-produced in sagd1 mutants, whereas posterior/auditory neurons develop normally. (J) Number of TUNEL+ apoptotic cells at the indicated times. sagd1 mutants show fewer apoptotic cells than normal at 24 and 30 hpf, indicating that the deficiency in vestibular SAG neurons is not due to cell death. Sample sizes are indicated (I, J). |