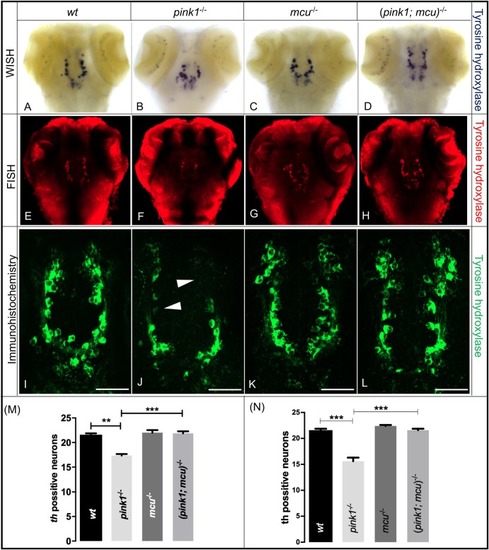
Dopaminergic neurons are rescuedafter deleting mcu in pink1−/− zebrafish. (A–D) Representative images of wt (A), pink1−/− (B), mcu−/− (C) and (pink1; mcu)−/− (D) 3 dpf larvae after WISH using TH-specific riboprobe. (E–F) Representative images of wt (E), pink1−/− (F), mcu−/− (G) and (pink1; mcu)−/− (H) 3 dpf larvae after whole-mount FISH using TH-specific riboprobe and TSA/Cy3-based signal amplification. There was a significant decrease (P<0.001) in number of dopaminergic neurons in pink1−/− zebrafish when compared to wt. In (pink1; mcu)−/− zebrafish there was a significant increase (P<0.05) in number of dopaminergic neurons when compared to pink1−/− zebrafish. (I–L) Representative images of wt (I), pink1−/− (J), mcu−/− (K) and (pink1; mcu)−/− (L) 3 dpf larvae after immunohistochemistry using TH-specific antibody. Arrowheads show absence of dopaminergic neurons. (M) Graphical representation of chromogenic WISH. There was a significant decrease (**P<0.01) in number of dopaminergic neurons in pink1−/− zebrafish when compared to wt. In (pink1; mcu)−/− zebrafish, there was a significant increase (***P<0.001) in number of dopaminergic neurons when compared to pink1−/− zebrafish. (N) Graphical representation of immunohistochemistry. There was a significant decrease (***P<0.001) in number of dopaminergic neurons in pink1−/− zebrafish when compared to wt. In (pink1; mcu)−/− zebrafish there was a significant increase (***P<0.001) in number dopaminergic neurons when compared to pink1−/− zebrafish. The mean number of diencephalic dopaminergic neurons for wt, pink1−/−, mcu−/− and (pink1; mcu)−/− was calculated over three independent experiments (n=10 embryos per genotype and experiment). Scale bars: 100 μm.
|

