|
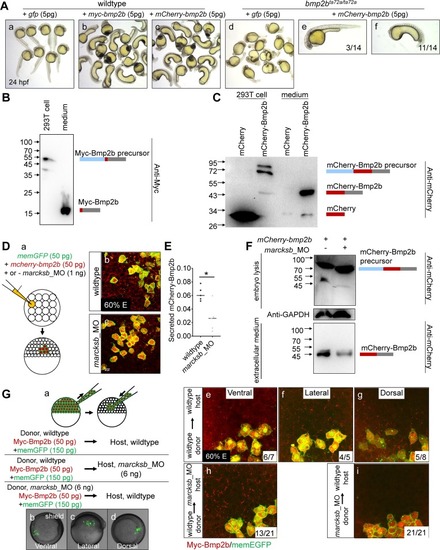
Marcksb cell autonomously regulates the extracellular level of Bmp2b.(A) Injection of either myc-bmp2b or mcherry-bmp2b caused severe ventralization at 24 hpf, and injection of mcherry-bmp2b could rescue the dorsalization of bmp2b mutant. (A-a) wildtype embryos; (A-b) myc-bmp2b injected embryos; (A-c) mcherry-bmp2b injected embryos; (A-d) bmp2b mutant (allele name: bmp2bta72a/ta72a); (A-e) representative imaging showing mcherry-bmp2b rescued bmp2bta72a/ta72a; (A-f) representative imaging showing ventralized bmp2bta72a/ta72a by over-dosage of mcherry-bmp2b. All embryos were at 24 hpf. (B) The pCS2-myc-bmp2b plasmid was transfected into 293T cells. Intracellular and extracellular Myc-Bmp2b were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Myc antibody. The positions of precursor and mature Bmp2b are illustrated schematically to the right of each gel. (C) The pCS2-mcherry-bmp2b plasmid and pCS2-mcherry plasmid were transfected into 293T cells separately. Intracellular and extracellular mCherry-Bmp2b or mCherry were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-mCherry antibody. The positions of mCherry-Bmp2b precursor, mature mCherry-Bmp2b and mCherry alone are illustrated schematically to the right of each gel. (D) Knockdown of marcksb reduced the extracellular level of Bmp2b. (D-a) showed a diagram of mosaic injection; (D-b) showed the extracellular level of mCherry-Bmp2b in wildtype embryos; (D-c) showed the extracellular level of mCherry-Bmp2b was significantly reduced in the marcksb morphant embryos. (E) Quantitative measurement of secreted Bmp2b in wildtype and marcksb morphant embryos. The data were presented as scatter plots with median; *”: P < 0.01, from Student’s t-test. (F) The mCherry-bmp2b mRNA injected wildtype embryos and marcksb morphants were collected separately at shield stage. Total cell-derived and extracellular mCherry-Bmp2b were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-mCherry antibody. The positions of mCherry-Bmp2b precursor and mature mCherry-Bmp2b are illustrated schematically to the right of each gel. (G) Assay on secreted Myc-Bmp2b of wildtype cells and marcksb-depleted cells by transplantation. (G-a) A diagram of cell transplantation; (G-b, c, d) The transplanted embryos at shield stage, indicating the location of transplanted cell populations: ventral (b), lateral (c) and dorsal (d); (G-e, f, g) When wildtype donor cells were transplanted into wildtype host, the extracellular Myc-Bmp2b were at a comparable level among ventral (e), lateral (f) and dorsal transplants (g); (G-h) When wildtype donor cells were transplanted into the marcksb morphants, the extracellular Myc-Bmp2b was not reduced; (G-i) When the marcksb morphants cells were transplanted into wildtype host, the extracellular Myc-Bmp2b was strongly inhibited.
|