|
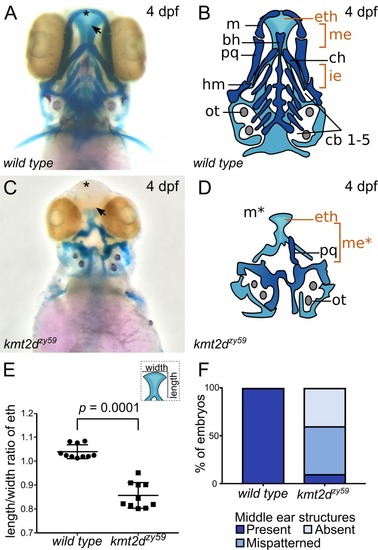
<italic>kmt2d</italic> mutants exhibit anomalous palate development and middle ear structures defects.(A-D) Alcian Blue/Alizarin Red staining of cartilage and bone showing zebrafish homologous structures for mammalian palate (neurocranium) and middle ear (jaw structures). Ventral view of zebrafish sibling control (A) and kmt2dzy59 mutant (C) embryos at 4 dpf with corresponding simplified cartoons (B, D). kmt2dzy59 mutants had severe hypoplasia of visceral cartilages (C; dark blue, D) and neurocranium (C; light blue, D) when compared with wild-type siblings (A, B). The ethmoid plate was present but displayed abnormal development (eth). The cartilages that pattern the jaw in the mandibular (m, pq) and hyoid (ch, hm) arches were absent (m*) or drastically reduced. Pharyngeal arches were absent (cb1-5). The specific structures that are considered mammalian homologs of palate and middle ear are highlighted in orange (eth, me). (E) Quantification of width/length ratio of the ethmoid plate in wild-type siblings and kmt2dzy59 mutants. In all mutant embryos analyzed, the ethmoid plate was present but had a significantly reduced length/width ratio when compared with wild-type siblings. Statistical analysis was carried out using two-tailed t test, p < 0.0001, n = 10 per genotype. Values for each data point can be found in S1 Data. (F) Embryos were classified according to the degree of development of homolog structures for mammalian middle ear. The categories were present, mispatterned, or absent. Qualitative assessment was plotted for percentage of embryos per genotype (n = 10 per genotype). Values for each data point can be found in S1 Data. bh, basihyal; cb, ceratobranchial; ch, ceratohial; dpf, days post fertilization; eth: ethmoid plate; hm, hyomandibula; ie, inner ear; m, Meckel’s; me, middle ear mammalian homologs; ot, otolith; pq, palatoquadrate.
|