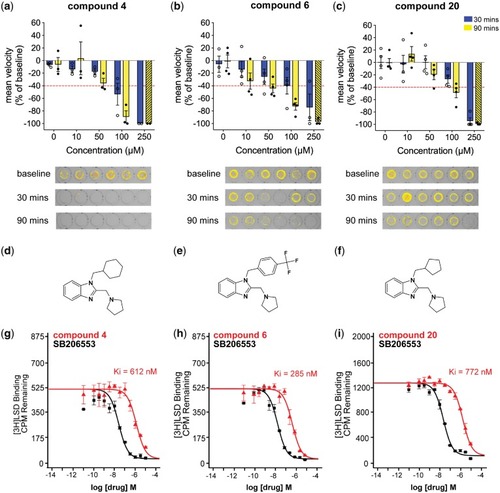
Evaluation of clemizole analogues that reduce seizure-like swim behaviour in scn1lab mutant zebrafish. Clemizole analogues identified as positive from the in vivo screen were freshly synthesized and retested for efficacy in suppressing the seizure-like swimming behaviour of 5 dpf scn1Lab mutant zebrafish. Graphs show the change in mean velocity over four concentrations of (a) compound 4, (b) compound 6 and (c) compound 20. Each bar represents the mean change in velocity ± SEM from three independent experiments (six individual larva per experiment). Toxicity is indicated by dashed bars. The threshold for a decrease in velocity is ≥40% (red line). Locomotion of larvae was recorded for 10 min after an exposure of 30 min (blue bars) and 90 min (yellow bars). A representative raw 10 min tracking plot is shown for a single experiment of six individual scn1Lab zebrafish. The chemical structure for each clemizole analogue is shown (d–f). In vitro radioligand binding analyses of (g) compound 4, (h) compound 6 and (i) compound 20 revealed specificity for 5-HT2BR over 5-HT2R subtypes. SB206553 was used as a positive control for 5-HT2BR binding (black). The binding affinity for the other clemizole analogues is given in Supplementary Table S2.
|