Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-181206-9
- Publication
- Ahlberg et al., 2018 - Rare truncating variants in the sarcomeric protein titin associate with familial and early-onset atrial fibrillation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
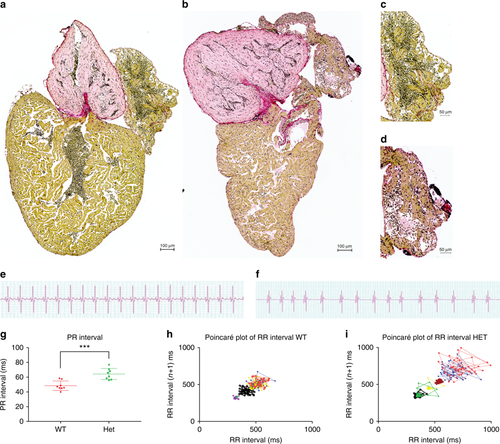
Truncating mutation in ttn.2 cause increase fibrosis and electrophysiological defects in adult heterozygous mutants. Sirius staining of isolated whole hearts from adult WT (a) and heterozygous mutant siblings (b) show increased fibrotic lesions in the heterozygous heart (b) compared with the WT (a). This increase appears to be more pronounced in the atria of the heterozygous hearts (d) (n = 4) compared with that of the WT siblings (c) (n = 4). Scale bars: a, b 200 µm; c, d; 50 µm. ECG surface recordings of adult WT fish (e) revealed a regular ECG pattern with well-defined P-waves and QRS complexes, with regular PR intervals (g) and RR intervals, with low beat-to-beat variability, as shown by the Poincaré plot (h), indicative of a regular heart rhythm (n = 8). In the heterozygous siblings, the ECG pattern was equally well defined (f), but with a larger PR interval, compared with the WT siblings. Furthermore, the RR interval and beat-to-beat variability was irregular, as demonstrated by the Poincaré plot (i), indicating an irregular heart rhythm in the heterozygous siblings (n = 8) |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |