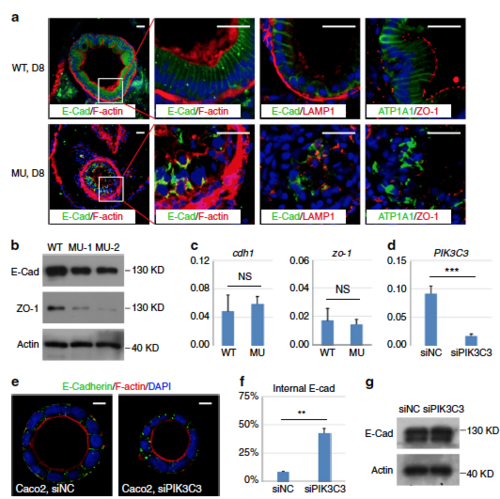
PIK3C3 deficiency induces polarity defects in IECs. a Immunofluorescence staining of gut cross sections at 8 dpf. In WT embryos, columnar IECs are arranged into a sheet and E-Cadherin are laterally distributed. IECs become disorganized and E-Cadherin is endocytosed and forms intracellular aggregates in the mutants. LAMP1 is a lysosome marker and it does not co-localize with E-Cadherin aggregates. Other polarity-related proteins including Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 subunit (ATP1A1) and tight junction protein ZO-1 also lose their polarized distributions in the mutant guts. Scale bar, 20 µm. b Western blot analysis for the expression levels of E-Cadherin and ZO-1 in the dissected digestive tracts from 8 dpf embryos. Beta actin is the loading control. c qRT-PCR analysis of cdh1 and zo-1. Assays are performed as described in Fig. 3f. d Knockdown efficiency of PIK3C3 by siRNA in Caco2 cells as determined by qRT-PCR. ACTB is the internal control and data represent mean ± SD from three biological repeats (***p < 0.001 by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). e PIK3C3 knockdown induces internalization of E-Cadherin in Caco2 cyst cultured on 3D Matrigel. Scale bar, 10 µm. f Quantification of (e). In each experiment, about 100 cysts were analyzed and data represent mean ± SD of the percentages of cyst with internalized E-Cadherin from three biological repeats (**p < 0.01 by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). g Western blot analysis of E-Cadherin protein levels in control or siPIK3C3-treated Caco2 cells. Beta actin is the loading control
|

