Fig. 1
|
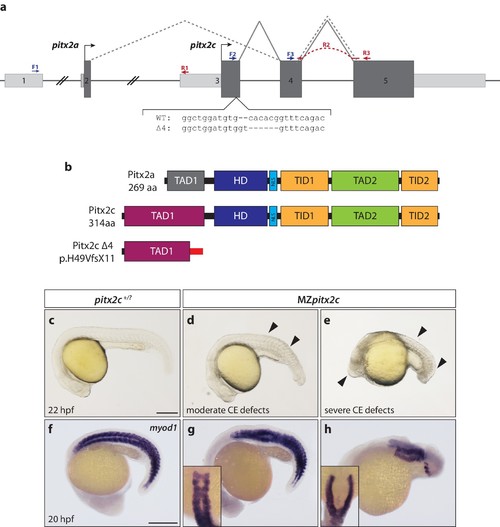
Maternal and zygotic Pitx2c function are required for embryonic development. (a) Schematic of the zebrafish pitx2 locus including the sequence of the Δ4 allele. The location of forward (F) and reverse (R) primers used for qPCR are indicated in blue and red, respectively. The red dashed line for R2 indicates primer binding on the 3’ end of exon 4 and the 5’ end of exon 5. The gray dashed line indicates splicing of the pitx2a isoform, while the solid line indicates splicing of the pitx2c isoform. (b) Schematic of the domains of Pitx2a, Pitx2c, and the predicted truncated protein generated from the Δ4 transcript. (c–h) Phenotypes observed in MZpitx2c mutant embryos obtained from homozygous mutant incrosses compared to wild-type embryos. MZpitx2c mutant phenotypes are variable and can be classified into three groups: Class I embryos exhibit somite defects (d, g); Class II embryos exhibit severe axis shortening and other malformations suggestive of convergence and extension (CE) defects (e, h); Class III embryos exhibit no obvious morphological defects (not shown). HD: homeodomain; NLS, nuclear localization signal; TAD: transactivation domain; TID, transactivation inhibitory domain. Scale bars, 250 μm. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | 20-25 somites |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | 20-25 somites to 26+ somites |