Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180522-38
- Publication
- Fadeev et al., 2018 - ALKALs are in vivo ligands for ALK family receptor tyrosine kinases in the neural crest and derived cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
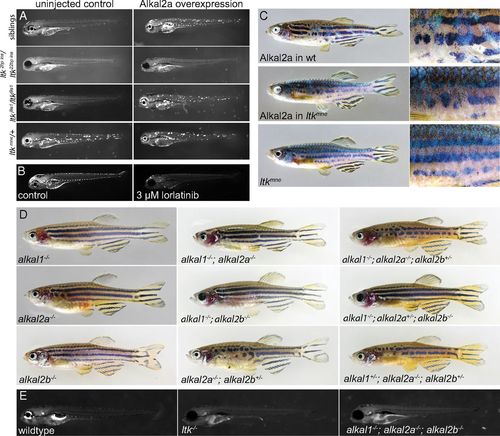
DrAlkals affect iridophore development via DrLtk. (A) Ectopic expression of DrAlkal2a does not rescue loss of iridophores in 4 dpf transheterozygous ltk knockout zebrafish larvae (2 bp insertion/22 bp insertion, n = 9/9), whereas in heterozygous or wild-type siblings and ltkj9s1 larvae, it leads to overproduction of iridophores (n = 29/29 and 34/35). Overexpression of DrAlkal2a in ltkmne mutant slightly enhances the phenotype. (B) Treatment with lorlatinib results in diminished iridophore numbers in 4 dpf larvae. (C) Mosaic overexpression of DrAlkal2a produces patches of supernumerary iridophores in wild-type and ltkmne adults. Overexpression of DrAlkal2a in ltkmne mutants enhances production of supernumerary iridophores compared with uninjected ltkmne. (D) Zebrafish alkal mutants display defects in iridophore development. alkal1ko mutants have reduced iridophores in eyes and operculum, and removal of both alkal1and alkal2b results in a complete loss of eye iridophores. alkal2ako mutants show the strongest phenotype, with reduced numbers of iridophores in the trunk, especially anteriorly. This phenotype displays increased penetrance in alkal2a;alkal2b double mutants. (E) Triple mutant for all alkal genes is embryonic lethal and displays total loss of iridophores, similar to ltk transheterozygous knockout. |