Fig. 2
|
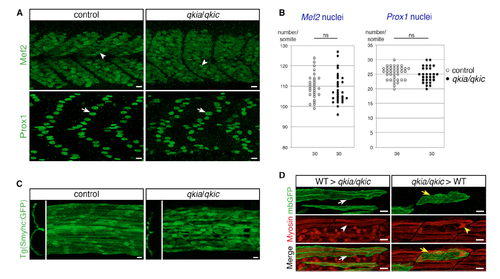
qkia and qkic Control Cells Autonomously Slow Muscle Cell Differentiation (A) Slow muscle cells in embryos with impaired qkia and qkic function are specified. Confocal imaging with z projection of Mef2 and Prox1-immmunostained 26-hpf zebrafish embryos (lateral view). Mef2 is expressed similarly in slow (arrowheads) and fast muscle cells of control (sibling from intercrosses of qkia+/−;qkic+/− parents, n = 10) and qkia−/−;qkic−/− embryos (n = 10). Slow muscle cells also express Prox1 (arrows) similarly in control (WT or qkia+/− embryos injected with control MO, n = 32) and qkia−/− embryos injected with qkic MO (n = 24). (B) Quantification of Mef2 and Prox1 positive nuclei illustrated in (A). The number of Mef2-positive cells in control (sibling from intercrosses of qkia+/−;qkic+/− parents, n = 10 embryos) and qkia−/−;qkic−/− embryos (n = 10 embryos) is similar (Student's t test, p = 0.49). qkia−/− embryos injected with qkic MO also have a similar number of Prox1-positive cells (n = 12 embryos) as qkic MO-injected qkia−/− embryos (n = 10 embryos) (Student's t test, p = 0.32). Numbers under the graph indicate the total number of quantified somites. ns, not significant. (C) Slow muscle cells in embryos with impaired qkia and qkic function are correctly located within the somite. Confocal imaging of 26-hpf tg(Smyhc:GFP) zebrafish embryos (endogenous fluorescence) in reconstructed transverse view (left panel) or lateral view with z projection (right panel). Slow muscle cell migration toward the somite surface is not affected in qkia−/− embryos injected with qkic MO (n = 48) compared with control (sibling embryos injected with control MO, n = 54). (D) qkia and qkic control slow muscle myofibril formation cell autonomously. Transplantation of WT mbGFP-expressing slow muscle precursors into a qkia/qkic embryo (left panel) and qkia/qkic slow muscle precursors into a WT embryo (right panel). See STAR Methods for details. Confocal imaging with z projection of GFP (green) and myosin (red) immunostained 26-hpf zebrafish embryos (lateral view). WT slow muscle cells (white arrows) develop normal myofibrils (white arrowhead) in qkia/qkic embryos (n = 28 cells) whereas qkia/qkic cells (yellow arrows) form myosin aggregates (yellow arrowhead) in WT embryos (n = 19 cells). In all panels, anterior is to the left. Scale bars, 10 μm. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Antibodies: | |
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 42(5), Bonnet, A., Lambert, G., Ernest, S., Dutrieux, F.X., Coulpier, F., Lemoine, S., Lobbardi, R., Rosa, F.M., Quaking RNA-Binding Proteins Control Early Myofibril Formation by Modulating Tropomyosin, 527-541.e4, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell