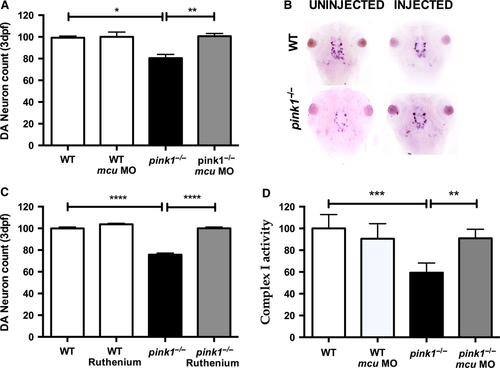
Knockdown of mcu leads to rescue of dopaminergic neurons. (A) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt MCU (wt microinjected with MO against mcu), pink1−/−, pink1−/− MCU (pink1−/− microinjected with MO against mcu) zebrafish larvae at 3 dpf. DA neuronal cell count is reduced in pink1−/− (*P = 0.012) but completely rescued after MCU inactivation (**P = 0.0085). The scale on the y axis reflects % of DA neurons compared to wt controls. (B) Representative image showing dopaminergic neurons in the diencephalon [using tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) whole mount in situ (WISH) staining] in wt controls and pink1−/− zebrafish injected with and without mcu MO. (C) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt embryos treated with Ruthenium red (RR) (wt RR), pink1−/− and pink1−/− embryos treated with RR (pink1−/− RR) with complete rescue of DA neurons in pink1−/− larvae after RR treatment (****P < 0.0001). The scale on the y axis reflects % of DA neurons compared to wt controls. (D) WT vs pink1−/− (***P = 0.0007). Mitochondrial complex I activity is restored in 5 dpf pink1−/− following mcu k/d (**P = 0.0071). Complex I activity is measured in μmol oxidized NADH per 1 unit of citrate synthase activity and set to 100% for the complex I activity in WT controls. The scale on the y axis reflects % of complex I activity compared to wt controls.
|

