Fig. S6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170914-32
- Publication
- Scott et al., 2017 - Nuclear/cytoplasmic transport defects in BBS6 underlie congenital heart disease through perturbation of a chromatin remodeling protein
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
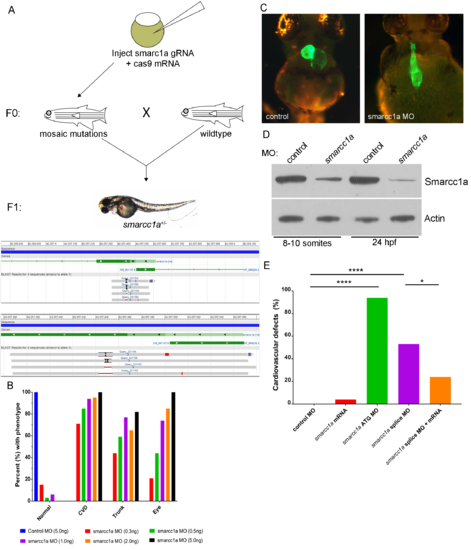
Smarcc1a knockout/knockdown causes cardiac phenotypes. Attempts to generate smarcc1a knockout zebrafish are unsuccessful because smarcc1a heterozygous fish, in the F1 generation, do not survive to breeding age (A). Smarcc1a knockdown with a translation blocking (ATG) morpholino (MO) causes multiple development phenotypes in the zebrafish in a dose dependent manner; phenotypes match smarcc1a heterozygous mutants (B). Heart labeled using transgenic line expressing GFP in differentiated cardiac tissue, Tg(myl7:EGFP) (C). Western blot for total protein validating that a human SMARCC1 antibody cross-reacts with zebrafish smarcc1a; reduced levels are observed in smarcc1a knockdown (0.5ng of MO) embryos compared to control MO injected embryos; Actin was used as a control (D). Percent of zebrafish larvae displaying cardiovascular defects from control MO, smarcc1a ATG MO, smarcc1a splice block MO, and smarcc1a splice block MO + smacc1a mRNA; fishers exact test used to compare groups, p-values: * < 0.05, **** <0.0001 (E). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |