Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170320-6
- Publication
- Ramspacher et al., 2015 - Developmental Alterations in Heart Biomechanics and Skeletal Muscle Function in Desmin Mutants Suggest an Early Pathological Root for Desminopathies
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
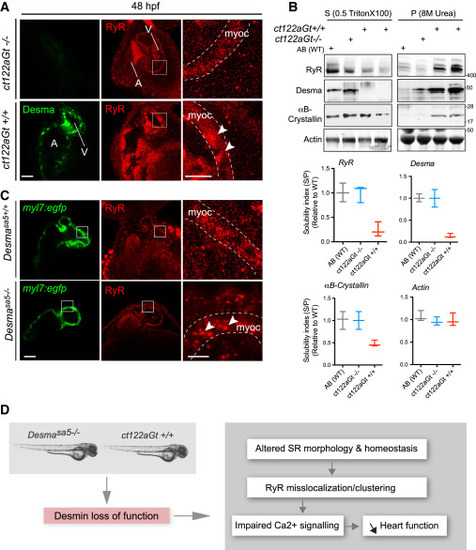
Desma Aggregation or Loss of Function Impact on Ryanodine Receptor Localization (A) Confocal images of RyR (red) in cardiac muscle from 48-hpf embryos showed homogenous and regular labeling mostly in the myocardium (myoc, highlighted with the white dotted lines) in control fish (ct122aRGt−/−), while in desma ct122aRGt+/+ mutant hearts RyR display irregular localization and clustering (white arrowheads). Scale bar, 30 μm.(B) In support of (A), RyR solubility was reduced in ct122aRGt+/+ mutant fish extracts compared to control where the majority of RyR fraction remains in the Triton X-100 fractions. αΒ-crystallin solubility is also affected in ct122aRGt+/+ embryos. Actin is the loading control. Bars showed quantification from two independent experiments, and each sample contains a mixture of 50–100 fish. (C) Similar to (A), confocal images of cardiac muscle from 48-hpf embryos in desmasa5−/− animals crossed with the myocardium-specific Tg(myl7:egfp) (green) line compared to controls (Tg(myl7:egfp; desmasa5+/+)) showing mislocalization and clustering (white arrowheads) of RyR in the myocardium (myoc, highlighted with the white dotted lines). Scale bar, 30 μm. myoc, myocardium (D) Schematic drawing of how desma loss of function (knockout or aggregation) could impact sarcoplasmic reticulum shape and EC-coupling machinery particularly on RyR localization. The error bars correspond to the SEM. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |