Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160812-1
- Publication
- Kim et al., 2014 - Developmental roles of D-bifunctional protein-A zebrafish model of peroxisome dysfunction
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
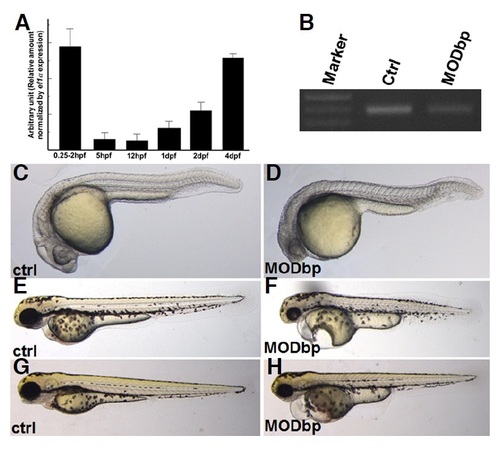
dbp expression is essential for zebrafish embryogenesis. (A) dbp expression during development. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to assay dbp expression during development. The highest expression of dbp is at 0-2 hpf (maternally deposited) after which it is significantly decreased but increased gradually at 1dpf onwards. The graph shows relative amount of dbp mRNA normalized by ef1± expression. (B) dbp splicing-blocking morpholino (MO) efficiently reduced synthesis of mature mRNA. Total RNA extracted from control and MO-injected embryos at 1 dpf were used for cDNA synthesis followed by RT-PCR. A ~ 390 bp band in the control lane was significantly reduced in the morpholino-injected lane (MODbp), indicating high efficiency of MO. (C-H) dbp knockdown generates morphologically distinct phenotypes. MO-injected embryos displayed phenotypes, includingsmall head, pericardial edema, and voluminous yolk compared to control embryos [compare (C, E, and G) with (D, F, and H)]. As embryogenesis continued, phenotypes became more severe [(C) and (D) (1dpf); (E) and (F) (2 dpf); (G) and (H) (3 dpf)]. Embryos are shown in lateral view with anterior to the left. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage Range: | 1-cell to Day 4 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Protruding-mouth |