Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150827-15
- Publication
- Sun et al., 2014 - Human Kidney Disease-causing INF2 Mutations Perturb Rho/Dia Signaling in the Glomerulus
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
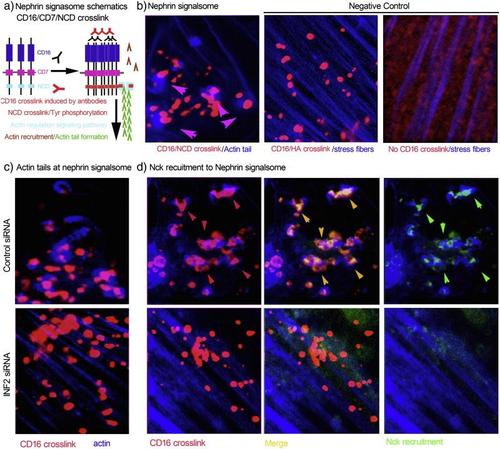
INF2 depletion in cultured podocytes destroys the integrity of slit diaphragm signaling. a. Schematic of CD16/Nephrin cytoplasmic domain (NCD) crosslink model. In cultured human podocytes expressing recombinant CD16/CD7/NCD, anti-CD16 antibody and Alexa Fluor594-conjugated secondary antibody were applied to induce CD16/NCD crosslink. The crosslink leads to phosphorylation of Tyr residuals in NCD, recruitment of Nck and actin remodeling. b. The successful crosslink exhibits blue actin tails attached to red nephrin signalsome particles. Podocytes expressing CD16/CD7/HA with CD16 crosslinked (no actin tails attaching to CD16/HA crosslink particles) and podocytes expressing CD16/CD7/NCD without CD16 crosslinked served as two negative controls. c. In podocytes expressing CD16/CD7/NCD, INF2 knockdown disrupts GFP-Nck recruitment (d) the actin tail formation (c and d) despite successful crosslinking, leading to loss of normal of slit diaphragm signaling. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |