Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150824-13
- Publication
- Helker et al., 2015 - The hormonal peptide Elabela guides angioblasts to the midline during vasculogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
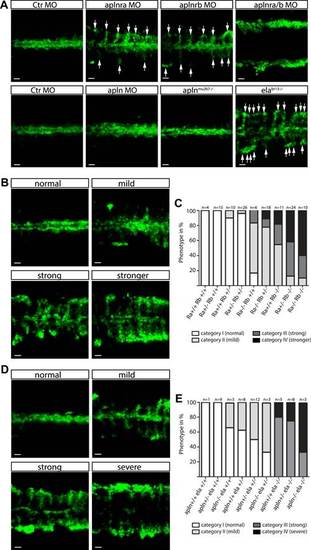
Ela/Apelin receptor - signaling guides angioblast migration to the midline. (A) Angioblasts have migrated to the midline at 17 hpf in wild type, aplnmu267 mutant or apln MO injected zebrafish embryos. MO-mediated knockdown of apelin receptor a or b partially inhibited midline migration, while simultaneous loss of both apelin receptor genes completely abolished midline migration of angioblasts. Likewise, embryos with homozygous mutations in the ligand ela display impaired migration of angioblasts. Arrows indicate aberrant positions. (B, C) Mutations in apln receptor genes impair angioblast migration. Analysis of the offspring of aplnra+/;aplnrb+/ double heterozygous parents resulted in four phenotypic categories (normal, mild, strong, stronger). (B) Genotyping of individual embryos revealed an additive effect, while mild phenotypes were observed when one receptor gene was homozygously mutant, phenotypic strength increased with additional loss of functional receptor genes (c; Ra, aplnra; Rb, aplnrb). (D, E) Ela deficiency can partially be compensated by Apln. Analysis of the offspring of apln+/;ela+/ double heterozygous parents resulted in four phenotypic categories (normal, mild, strong, severe). (D) Genotyping of individual embryos revealed a dose dependency, with increasing phenotypic strength correlating with additional loss of apln alleles in ela mutant embryos. (E) ela/; apln/ double mutants phenocopied apln receptor deficiency. Angioblasts (green) were labeled by Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 expression, scale bars represent 30 µm. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 14-19 somites |