Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140527-10
- Publication
- Steiner et al., 2014 - Dynamic gene expression by putative hair-cell progenitors during regeneration in the zebrafish lateral line
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
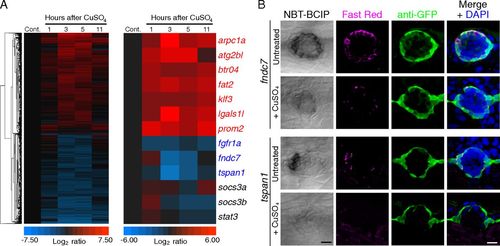
Transcriptional response of mantle cells to hair-cell destruction. (A) Extirpation of hair cells by the ototoxic chemical CuSO4 evokes the dynamic expression of select candidate genes in sorted mCh+ cells. Microarray results from samples dissected 1, 3, 5, and 11 h after treatment were normalized to those from untreated control samples (Cont.). (Left) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of all of the genes whose expression was up- or down-regulated by at least a factor of 2 at some time after treatment, except genes whose expression also changed in NF cells. (Right) Genes of interest were selected on the basis of the degree and significance of differential expression as well as the availability of reliable annotation. The genes listed in blue were primarily down-regulated following hair-cell ablation, whereas those shown in red were principally up-regulated. The genes labeled in black were previously reported to be up-regulated in the sound-damaged zebrafish inner ear (42). (B) In situ hybridization supports the results from microarrays and reverse-transcription qPCR analyses: Both fndc7 and tspan1 are enriched in mantle cells and demonstrate reduced expression following CuSO4 treatment. The first column displays the results of chromogenic in situ hybridization; the second and third columns compare FISH (Fast Red) with GFP immunoreactivity (green) in Et20 larvae. The merged images in the fourth column include nuclear staining with DAPI (blue). (Scale bars: 10 μm.) |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |