Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140414-10
- Publication
- Miyares et al., 2013 - Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
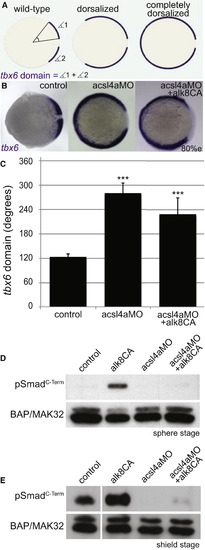
Acsl4a Acts Downstream of Bmp Receptor Activation (A) The extent of dorsalization is measured by adding the angles of the arcs of dorsal marker tbx6 expression on either side of the tbx6 negative midline at 80% epiboly. Embryos are considered completely dorsalized if the arcs meet on the ventral side. (B and C) Constitutively active Bmp receptor does not rescue the phenotype caused by acsl4a depletion. (B) tbx6 expression in a control embryo, embryo injected with acsl4a MO alone (750 fmol), or acsl4a MO combined with constitutively active alk8 (alk8CA, 1.5 ng) mRNA. Vegetal pole view, dorsal to the right (80% epiboly). (C) Quantification of tbx6 expression domain. Data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SE (n = 3–8; 12–80 embryos/experiment). ANOVA with Dunnett post hoc test; p < 0.0001, compared to control. (D and E) Western blots (n = 3) of C-terminally phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 (pSmadC-Term) from embryos injected with alk8CA mRNA (20-40 pg), acsl4a MO (500 fmol), or acsl4a MO and alk8CA mRNA combined. Anti-BAP/MAK32 is the loading control. (D) Lysates from sphere-stage embryos. (E) Lysates from shield-stage embryos. An extraneous lane between control and alk8CA is omitted. See also Figure S4. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 27(6), Miyares, R.L., Stein, C., Renisch, B., Anderson, J.L., Hammerschmidt, M., and Farber, S.A., Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo, 635-647, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell