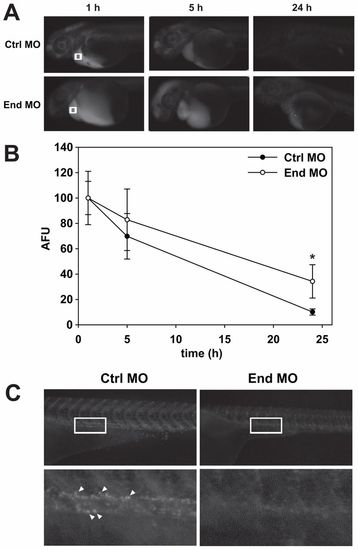
Pronephric kidney function is disrupted in endolyn morphants. (A) 1ng of 10kDa rhodamine-dextran was injected into the common cardinal vein of control (Ctrl) or endolyn (End) morphants at 48 hpf. Images were acquired under identical conditions at 1, 5 and 24h post-injection. (B) The loss of fluorescence over time near the common cardinal vein (regions marked by white boxes in A) was quantified, normalized to the initial fluorescence observed at 1h, and plotted. Three independent injections were quantified with at least ten Class I and control embryos injected in each experiment. At 24h, retained fluorescence is significantly greater in endolyn morphants compared with controls (*P = 0.001 by Mann–Whitney rank sum test). (C) Imaging of the pronephric proximal tubule 24h after injection of 70kDa rhodamine-dextran demonstrates impaired endocytosis in endolyn morphants. Bottom panels show enlarged regions of the areas delineated by white rectangles in the corresponding upper panels. Arrowheads point to examples of endocytic vesicles in control larvae.
|

