|
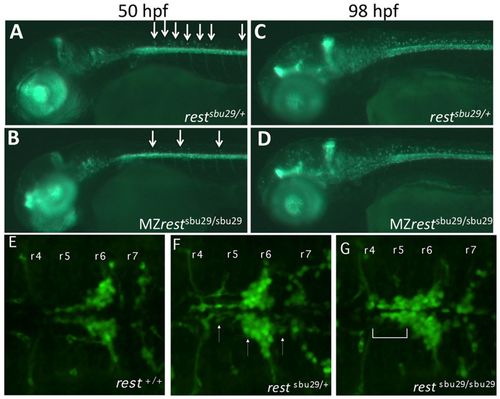
Rest function is crucial for the regulation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the dorsal spinal cord and for facial branchiomotor migration. (A-D) Lateral views of live 50-hpf and 98-hpf Tg(olig2:GFP) (A,C) and Tg(olig2:GFP); MZrestsbu29/sbu29 mutants (B,D). The number of migrating olig2+ oligodendrocyte precursors (arrows) is significantly reduced in rest mutants at 50 hpf (B) compared with controls (A). The number of migrating OPCs (arrows) in 98-hpf MZrestsbu29/sbu29 mutants (D) is similar to controls (C). (E-G) Dorsal views of the hindbrain of 48-hpf Tg(islet1:GFP) transgenic zebrafish embryos. Representative embryos from a restsbu29/+, restsbu29/+; islet1:GPF intercross. (E) rest+/+ embryo showing normal FBMN migration into r6-r7. (F) FBMNs in restsbu29/+ embryos have only subtle migration defects (arrows). (G) In restsbu29/sbu29 embryos, a significant proportion of FBMNs remain in r4-r5 (bracket).
|