Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120525-32
- Publication
- Jia et al., 2012 - Protein Phosphatase 4 Cooperates with Smads to Promote BMP Signaling in Dorsoventral Patterning of Zebrafish Embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
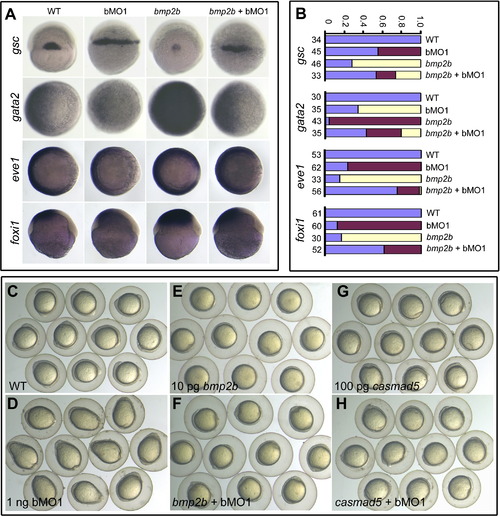
Genetic Interactions between Ppp4c and Components of the BMP Signaling Pathway (A and B) Marker alterations at the shield stage caused by 10 pg bmp2b mRNA or 1 ng ppp4cb-MO1 (bMO1) were mutually inhibited by their coinjection. gsc, dorsal views; gata2 and eve1, animal-pole views with dorsal to the right; foxi1, lateral views with dorsal to the right. Statistical data for marker expression are shown in (B). Blue, red, and yellow indicated normal, increased, and decreased expression levels, respectively. The number of observed embryos was indicated. (C–H) ppp4cb-MO1 (bMO1, 1 ng)-induced elongated shape at the bud stage was rescued by coinjection of bmp2b (10 pg) or casmad5 mRNA (100 pg) encoding constitutively active Smad5. See also Figure S3. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Shield |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Shield |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(5), Jia, S., Dai, F., Wu, D., Lin, X., Xing, C., Xue, Y., Wang, Y., Xiao, M., Wu, W., Feng, X.H., and Meng, A., Protein Phosphatase 4 Cooperates with Smads to Promote BMP Signaling in Dorsoventral Patterning of Zebrafish Embryos, 1065-1078, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell