Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111025-6
- Publication
- Link et al., 2000 - The zebrafish young mutation acts non-cell-autonomously to uncouple differentiation from specification for all retinal cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
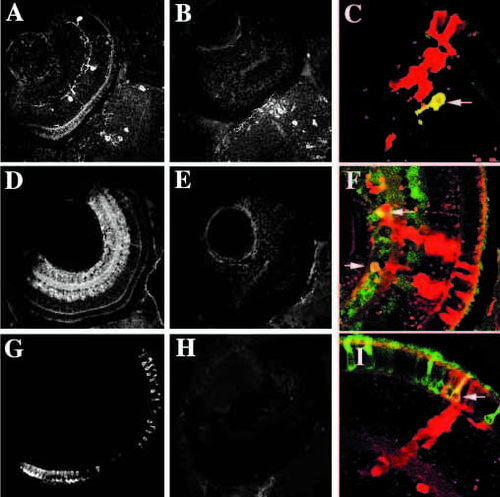
Rescue of expression of molecular markers in cells derived from young embryos when transplanted into wild-type retinas. (A-C) Tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactiviy (interplexiform cells) in wild-type (A), young (B) and chimeric (C) eyes. In chimeric eyes, young donor cells (red) can express tyrosine hydroxylase (yellow cell indicated with arrow). (D-F) GABA immunoreactivity (amacrine cells, primarily) in wild-type (D), young (E) and chimeric (F) eyes. In chimeric eyes, young donor cells (red) can express GABA (yellow cells indicated with arrows). (G, H, I) 1D1 (rod photoreceptors) in wild-type (G), young (H), and chimeric (I) eyes. In chimeric eyes, young donor cells (red) can express 1D1 (yellow cell indicated with arrow). |