Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-091113-77
- Publication
- Brend et al., 2009 - Expression of the oscillating gene her1 is directly regulated by hairy/enhancer of split, T-box, and suppressor of hairless proteins in the zebrafish segmentation clock
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
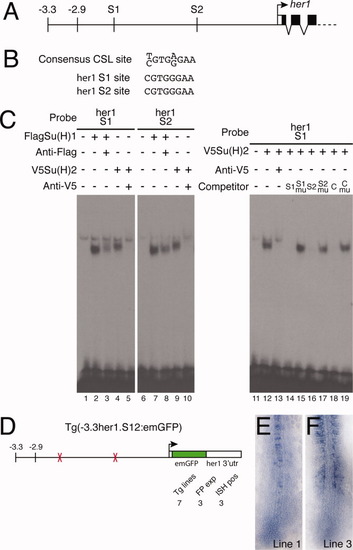
Su(H) binding sites within the -2.9-kb region are necessary for her1 expression. A: Representation of part of the her1 genomic locus indicating the position of the two Su(H) binding sites (S1 and S2). B: The S1 and S2 sequences are perfect matches for the consensus CSL binding site. C: Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) experiments confirm that the S1 and S2 sites bind both Su(H)1 and Su(H)2 (lanes 1-10). Control reactions contained unprogrammed lysate (lanes 1 and 6). A weak nonspecific complex is seen in every lane. Specificity of binding was confirmed by supershifting or blocking complexes with antibodies to the appropriate epitope tag (lanes 3, 5, 8, and 10). Recognition of specific sequences was confirmed by competition assays (lanes 11-19). Unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides were added at 100-fold molar excess. The C indicates the control oligonucleotide including the SPS motif from the mouse Hes1 gene; mu indicates competitors in which the CSL site was deleted (lanes 15 and 17) or mutated (lane 19). D: Schematic representation of the construct used to analyze the function of the two Su(H) binding sites. The total number of transgenic lines are indicated (Tg lines), as are the number of lines in which expression was detected by fluorescence (FP exp) and in situ hybridization (ISH pos). E,F: In situ hybridization of Tg(-3.3her1.S12:emGFP) embryos from two different lines showing expression of emGFP mRNA. |