Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090817-14
- Publication
- McMahon et al., 2009 - Lmx1b is essential for survival of periocular mesenchymal cells and influences Fgf-mediated retinal patterning in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
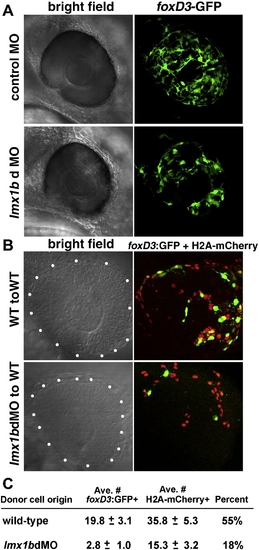
Lmx1b functions cell-autonomously in development of periocular mesenchymal cells. (A) Bright field and fluorescent images of control MO and lmx1bdMO eyes showing foxD3:GFP-positive periocular mesenchymal cells. (B) Ocular region (outlined by white dots) of 30 hpf mosaic embryos showing wild-type or lmx1bdMO morphant donors. All donor cell nuclei are positive for H2A:mCherry (red), while a subset of periocular cells are positive for foxD3:GFP (green). (C) Average number ± Standard Error of the Mean for total H2A:mCherry and foxD3:GFP-positive donor periocular cells from mosaic embryos. Percent of total periocular cells that were foxD3-positive is shown in the right-most column. For each condition, donor cells from n = 12 independent eyes were scored. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 332(2), McMahon, C., Gestri, G., Wilson, S.W., and Link, B.A., Lmx1b is essential for survival of periocular mesenchymal cells and influences Fgf-mediated retinal patterning in zebrafish, 287-298, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.