Fig. S3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090717-10
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2009 - The transcription factor six1a plays an essential role in the craniofacial myogenesis of zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
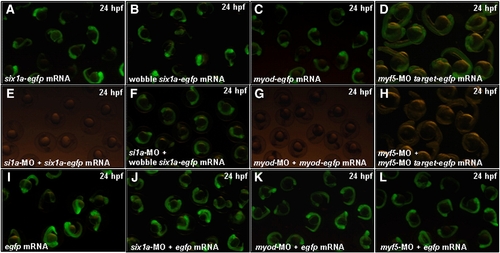
The confirmation of the specific activities of six1a-MO, myod-MO and myf5-MO in zebrafish embryos. Co-injection of six1a-MO (8 ng), myod-MO (4 ng) or myod-MO (4 ng) with its counterpart mRNA (100 pg) was employed into one-celled stage of zebrafish embryos. The Six1a-GFP fusion protein was detected at 24 hpf in embryos injected with a six1a-egfp mRNA (A). The Six1a-GFP fusion protein was not detected at 24 hpf in embryos co-injected with six1a-egfp mRNA and six1a-MO (E). The wobble Six1a-GFP fusion protein was detected at 24 hpf in embryos injected with a wobble six1a-egfp mRNA (B). The Six1a-GFP fusion protein was detected at 24 hpf in embryos co-injected with a wobble six1a-egfp mRNA and six1a-MO (F). The Myod-GFP fusion protein was detected at 24 hpf in embryos injected with myod-egfp mRNA (C). The Myod-GFP fusion protein was not detected in embryos co-injected with myod-egfp mRNA and myod-MO (G). Te GFP was detected in embryos injected with myf5-MO-targt-egfp mRNA at 24 hpf (D). The GFP signal was absent in embryos co-injected with myf5-MO-targt-egfp mRNA and myf5-MO (H). Embryos injected with egfp mRNA alone (I), co-injected with egfp mRNA and six1a-MO (J), egfp mRNA and myod-MO (K) and egfp mRNA and myf5-MO (L) served as control groups. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 331(2), Lin, C.Y., Chen, W.T., Lee, H.C., Yang, P.H., Yang, H.J., and Tsai, H.J., The transcription factor six1a plays an essential role in the craniofacial myogenesis of zebrafish, 152-166, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.