Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090710-57
- Publication
- Yabe et al., 2009 - The maternal-effect gene cellular island encodes aurora B kinase and is essential for furrow formation in the early zebrafish embryo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
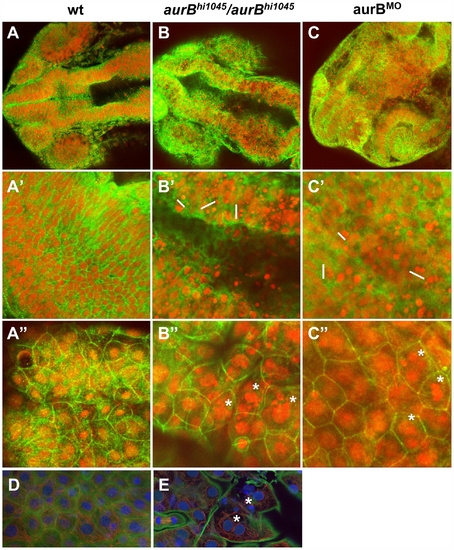
Cytokinesis defects in embryos lacking zygotic aurB function. (A–C″) Wild-type (A), aurBhi1045 homozygote (B) and aurB morphant (C) embryos fixed at 24 hours p.f. and labeled to detect β-catenin (green) and DNA (red). (A–C) Overview of the head region. (A′–C′) Optical section through the brain region, showing internal cells. aurBhi1045 homozygotes and aurB morphants show a high frequency of compact nuclei which are typically arranged in pairs (some examples indicated with a white bar at their left flank), consistent with cell death after a failure to undergo proper cytokinesis. (A″–C″) Optical section through a surface layer of the same region, corresponding to the EVL or peridermal layer. In this layer, cells in aurBhi1045 homozygotes and aurB morphants show a high frequency of multilobular nuclei (some examples indicated by asterisks), again suggestive of defects in cytokinesis. Wild-type embryos injected with control MO exhibit normal cellular and nuclear morphologies (not shown), similar to those observed in untreated wild-type embryos (A). (D–E) High magnification images of a wild-type (D) and aurBhi1045 homozygous (E) embryos labeled to detect β-catenin (green), microtubules (red) and DNA (blue). Mutant embryos exhibit closely apposed pairs of nuclei (asterisks) that lack an intervening adhesive membrane. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |