Fig. 6
|
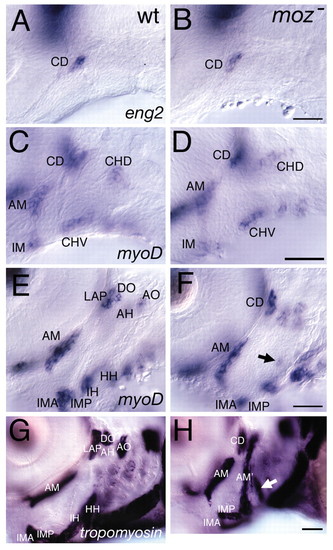
Late, but not early, muscle defects in moz mutants. (A,B) eng2 expression in wild types marks the dorsal first arch myogenic core, CD, which is not homeotically duplicated in moz mutants. (C-F) myod expression in wild type (C,E) and moz mutants (D,F) at 44 hpf (C,D) and 54 hpf (E,F). (C,D) myod expression marks three first arch and two second arch myogenic cores. The moz mutant second arch pattern at this stage appears normal. (E,F) By 54 hpf moz mutant musculature looks aberrant. A small ectopic patch of myod is present in the intermediate second arch (arrow in F). (G,H) Lateral views of α-tropomyosin expression in wild type (G) and moz mutant (H). In wild types (G), a large jaw closing muscle (am) connects the upper and lower jaw. moz mutants appear to have an ectopic jaw closer muscle (am′) in their second arch (H). This muscle appears continuous with what we interpret to be the remnants of the dorsal (AH and AO) and ventral muscles (IH and HH) and the first arch dorsal muscles (LAP and DO) appear to not have segregated as they have in wild types. An enlarged third arch muscle is present (white arrow in H) in moz mutants. AH, adductor hyomandibulae; AM, adductor mandibulae; AO, adductor operculi; DO, dilator operculi; HH, hyohyal; IH, interhyal; IMA, intermandibularis anterior; IMP, intermandibularis posterior; LAP, levator arcus palatini. Scale bars: 50 μm. |