Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070914-55
- Publication
- Rohrschneider et al., 2007 - Zebrafish Hoxb1a regulates multiple downstream genes including prickle1b
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
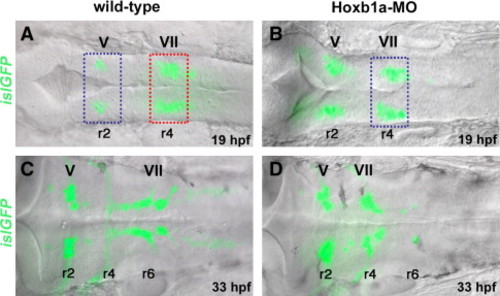
Microarray experimental strategy. islet1-GFP transgenic embryos in dorsal view, bright field (DIC optics) and fluorescent images merged. Anterior to the left in all panels. Rhombomeres (r) 2, r4, and r6 are labeled. (A, B) At 19–20 hpf, islet1-GFP-positive branchiomotor neurons are present in wild-type (A) and Hoxb1a-deficient embryos (B; injected with Hoxb1a-MO). Hoxb1a-positive tissue dissected from unmanipulated r4 (A, red box) was compared to Hoxb1a-deficient tissue dissected from r4 of Hoxb1a-MO injected embryos (B, blue box), and from unmanipulated r2 (A, blue box). (C, D) By 33 hpf, GFP-positive facial neurons have migrated into the posterior hindbrain of unmanipulated embryos (C), but remain in r4 of Hoxb1a-MO injected embryos (D). ov: otic vesicle; MO: morpholino; V: trigeminal neurons; VII: facial neurons. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 309(2), Rohrschneider, M.R., Elsen, G.E., and Prince, V.E., Zebrafish Hoxb1a regulates multiple downstream genes including prickle1b, 358-372, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.