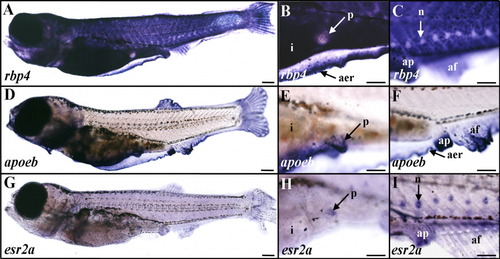
Expression of rbp4, apoeb, and esr2a in late zebrafish larva. A-C: rbp4. D-F: apoeb. G-I: esr2a. Whole-mount in situ hybridizations are shown in lateral views and anterior to the left with digoxigenin-labeled antisense riboprobes of 25-30 days postfertilization (dpf; 5.5-6 mm long) larvae. B,E,H and C,F,I are enlarged views of the pelvic fin-bud and anal papilla regions, respectively. A-C: rbp4 expression was detected in the epidermis and the apical ectodermal ridge (A,B), but not in pelvic fin buds (A,B) or neuromasts (C). D-F: apoeb transcripts were strongly expressed in pelvic fin buds (D,E) and the hybridization signal was detected in the apical ectodermal ridge, anal papilla, and elongating unpaired fin folds (D,F). G-I: esr2a transcripts were expressed in a diffuse manner in the epidermis (G-I), and in pelvic fin buds (H), and a strong signal was detected in neuromasts (I). af, anal fin; ap, anal papilla; apical ectodermal ridge, aer; i, intestine; n, neuromast; p, pelvic fin bud. Scale bars = 300 μm in A,D,G, 150 μm in B,C,E,F,H,I.
|

