Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-061121-10
- Publication
- Lyman Gingerich et al., 2006 - Analysis of axis induction mutant embryos reveals morphogenetic events associated with zebrafish yolk extension formation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
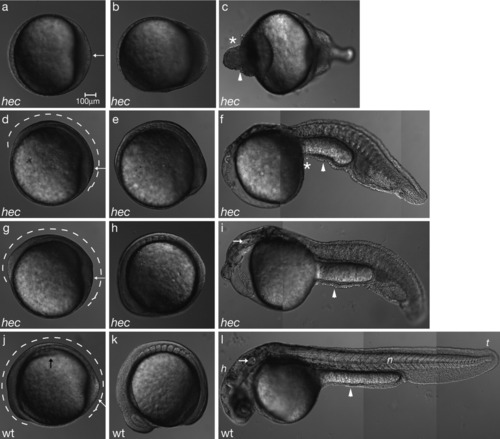
hec mutant embryos display morphogenesis defects consistent with the posteroventralization of cell fates. Radialized hec mutant embryos at the three-somite stage have an accumulation of cells at the tail bud (a, white arrow), whereas wild-type embryos already display a thickening of the dorsal side (j, black arrow) and elongation of the anterior-posterior axis (j, dotted line). The degree of enlargement of the posterior region and length of the anterior-posterior axis (a,d,g,j, white arrows and dotted lines, respectively) correlate with the phenotype at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf). a-c: During somitogenesis, radialized hec mutant embryos show an enlargement of the posterior tail bud followed by an accumulation of cells at the anterior end of the embryo (c, asterisk). d-f: Moderately affected mutants develop some dorsoanterior structures, but no head structures by 24 hpf. g-i: Mildly affected mutants develop more dorsoanterior structures, including posterior head structures such as the ear (white arrow in i), by 24 hpf. j-l: Wild-type embryos develop normal dorsoanterior structures, including a normal head and notochord by 24 hpf. (h, head; n, notochord; t, tail; white arrow in l: ear). Asterisks in c and f highlight cell accumulations in ventroposteriorized mutants. Arrowheads in c, f, i, and l point to constrictions in the embryos. Anterior, left; posterior, right; dorsal, top (when distinguishable). For each row, panels are still images from time-lapse microscopy analysis of the same embryo. |