- Title
-
Mutations affecting development of the zebrafish retina
- Authors
- Malicki, J., Neuhauss, S.C., Schier, A.F., Solnica-Krezel, L., Stemple, D.L., Stainier, D.Y., Abdelilah, S., Zwartkruis, F., Rangini, Z., and Driever, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Phenotypes of mutants characterized by eye specific pigmentation defect. (A) At 36 hpf pigmentation is apparent both in the eye and skin of wild-type embryos. In (B) glass onion (glo)m117, (C) oko meduzy (ome)m98, (D) heart and soul (has)m129 and (E) nagie oko (nok)m227, we observed abnormal differentiation of the pigmented epithelium. Melanocytes of these mutants have normal appearance although their development may be somewhat delayed. (F) Wild-type and (G) omem98 pigmented epithelium in living embryos. The eye pigmentation is uniform in the wild type and patchy in the mutant. Arrowheads indicate position of the choroid fissure. In all panels dorsal is up and anterior left. |
|
Transverse sections of mutant retinae at 3 dpf. The phenotypes of (A) oko meduzy (ome)m98, (B) glass onion (glo)m117 and (C) nagie oko (nok)m227 mutants are similar to each other. In the retinae of these mutants the plexiform matter forms patches instead of laminae. omem98 and nokm227 form a well differentiated optic nerves (arrowhead in A). (D) Retina of heart and soul (has)m129 mutant at 60 hpf. Although the optic nerve is present, the retina of hasm129 does not develop stratification. (E) one eyed pinhead (oep)m134, (F) cyclops (cyc)b16 and (G) bozozok (boz)m168 develop cyclopia. In these mutants retinal stratification develops to a limited degree. Abnormalities of the neuronal patterning are usually associated with presence of numerous cell corpses. (H) Some pandora (pan)m313 mutants develop normal neuronal lamination. The portion of the retina ventral to the optic nerve (arrowhead in H) is absent in panm313. In all panels ventral is down. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Head and trunk phenotypes of mutations predominantly affecting development of the outer retina. (A) Wild type. (B) mikre oko (mok)m632. (C) niezerka (nie)m743. (D) elipsa (eli)m649. (E) krenty (krt)m699. (F) sinusoida (sid)m604. Mutants in B, C, E and F have smaller eyes than the wild type. Eyes of elim649 have abnormal oval shape (D). The brain shape defect is most pronounced in krtm699. In all panels anterior is to the left and dorsal is up. All phenotypes were photographed at 5 dpf. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
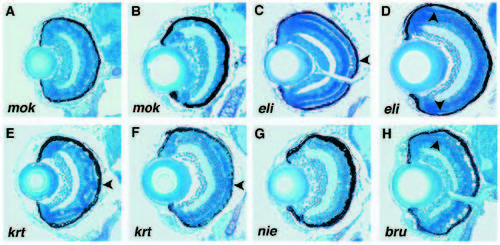
Phenotypes of mutations predominantly affecting development of the outer retina analyzed on histological sections (A) In mikre oko (mok)m632, a poorly differentiated photoreceptor cell layer is present in the central retina at 3 dpf. The presumptive photoreceptor cells frequently do not display the wild-type, elongated shape. (B) At 5 dpf, the photoreceptor cell layer is absent in mokm632. (C) The elipsa (eli)m649 retina at 3 dpf. Excessive cell death is most obvious in the central portion of the photoreceptor cell layer (arrowhead in C). (D) At 5 dpf most of the photoreceptor cells in elim649 are absent. Some cells survive in the periphery of the photoreceptor cell layer (arrowheads in D). (E) The krenty (krt)m699 retina at 3 dpf. The photoreceptor cell layer is discontinuous (arrowhead in E). Gaps in the array of photoreceptor cells appear to be filled with cells originating from the inner nuclear layer. This pattern persists till 5 dpf (F). (G) Retina of niezerka (nie)m743 at 5 dpf. The photoreceptor cell layer is missing. (H) brudas (bru)m148 retina at 3 dpf. As in elim649 some morphologically normal photoreceptors are present in the periphery (arrowhead in H). All sections are transverse. In all panels ventral is down. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
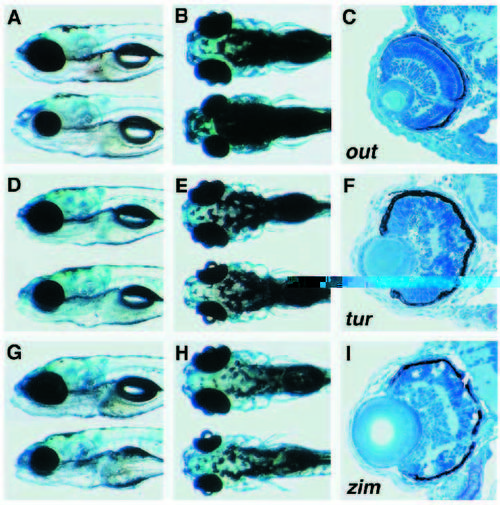
Examples of mutant phenotypes from the categories of Growth retardation and Nonspecific retinal degeneration. Mutant individuals (lower) are shown next to their wild-type siblings (upper). (A,B,C) out of sight (out)m233. (D,E,F) turbulent (tub)m125. (G,H,I) zimny (zny)m419. (A,B) The eye of outm233 is substantially reduced at 3 dpf. (C) All retinal laminae are present and cell death in excess of wild-type levels is not observed in outm233 at this stage. At 5 dpf mutants tubm125 (D,E) and znym419(G,H) are characterized by a reduced eye size and somewhat abnormal brain shape. Cell death is extensive in both tubm125 (F) and znym419(I) retinae at 3 dpf. Cell corpses appear as small, round, intensely staining particles (F). Retinal patterning defects are inconsistent in this group of mutants. A, D and G show lateral views; B, E and H dorsal views. The dorsal side is oriented up in panels showing lateral views or sections. In panels showing head phenotypes anterior is left. All sections are transverse. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Mutants involving retinal degeneration associated with a general pigmentation defect. Mutant individuals (lower) are shown next to their wild-type siblings (upper). (A,B,C) piegus(pgu)m286. (D,E,F) punktata(pkt)m288. (G,H,I) mizerny(miz)m293. All three mutants have abnormal melanocytes and reduced eye size. Sections through mutant retinae at 3 dpf (C,I) and 5 dpf (F) reveal an excessive amount of cell death. (J,K,L) Higher magnification of the dorsal retina in the wild type (J), pgum286 (K) and mizm293 (L). Cell corpses appear as small, round, intensely staining particles (arrows in K and L). In pktm288 and mizm293 the photoreceptor cell layer has abnormal appearance (F,I). A, D and G show lateral views; B, E and H dorsal views. The dorsal side is oriented up in panels showing lateral views or sections. In panels showing head phenotypes anterior is left. All sections are transverse. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|