- Title
-
Assessment of the Novel Anti-Seizure Potential of Validamycin A Using Zebrafish Epilepsy Model
- Authors
- Lee, E., Banik, A., Lee, K.B., Sim, S.M., Kil, A.H., Hwang, B.J., Kee, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Molecules
|
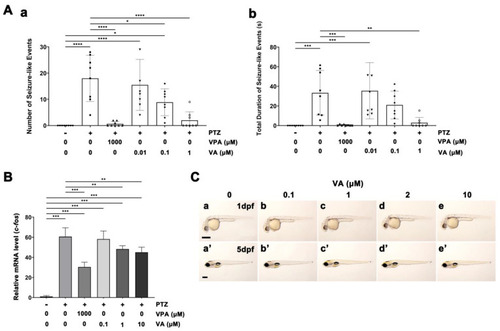
EEG analysis of anti-seizure efficacy of VA in the brains of PTZ-treated zebrafish larvae ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
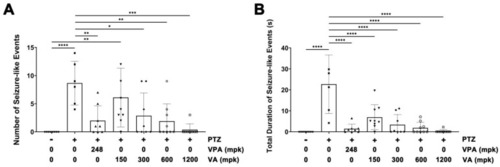
EEG analysis of the anti-seizure efficacy of VA in the brains of adult zebrafish administered PTZ. The collected data were represented graphically, depicting the total number of seizures ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Analysis of validamycin A’s efficacy in mitigating locomotive changes in adult zebrafish via measurements of angular velocity. ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
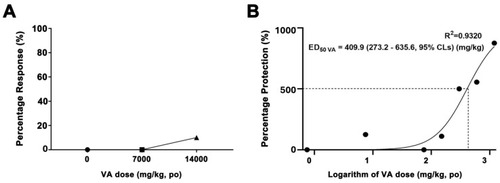
Quantification of the therapeutic dosage of validamycin A. ( |