- Title
-
Direct male development in chromosomally ZZ zebrafish
- Authors
- Wilson, C.A., Batzel, P., Postlethwait, J.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
Sex ratios and gonad histology in adult ZW and ZZ zebrafish at 5 months post fertilization (mpf). |
|
Developmental trajectory of gonads from ZW and ZZ fish. |
|
Cell-type marker genes for 19dpf ZW and ZZ gonads. |
|
Cell-type marker genes for 30dpf ZW and ZZ gonads. |
|
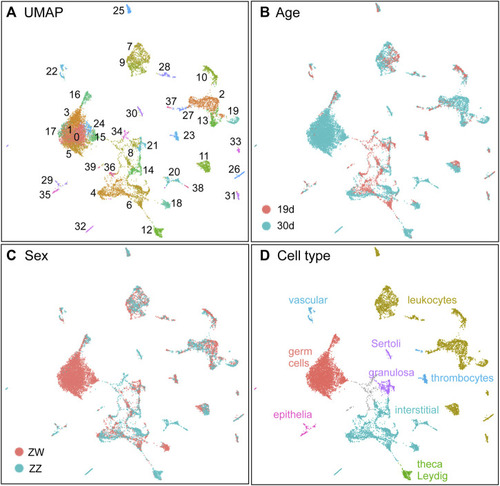
The combined dataset with two ages, each with two sex genotypes. |
|
Germ cell development in the merged analysis of both ZW and ZZ cells at both 19 and 30dpf. |
|
Support cell gene expression merging both time points and both sex genotypes. |
|
Steroidogenesis. |
|
Stromal/interstitial clusters. |
|
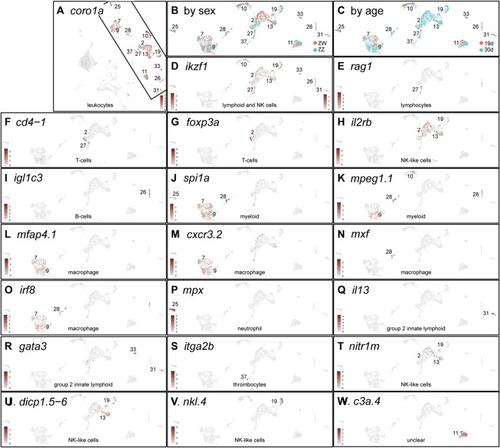
Immune cells. |