- Title
-
Establishment of a Dihydrofolate Reductase Gene Knock-In Zebrafish Strain to Aid Preliminary Analysis of Congenital Heart Disease Mechanisms
- Authors
- Gong, K., Xie, T., Yang, Y., Luo, Y., Deng, Y., Chen, K., Tan, Z., Guo, H., Xie, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cardiovasc Med
|
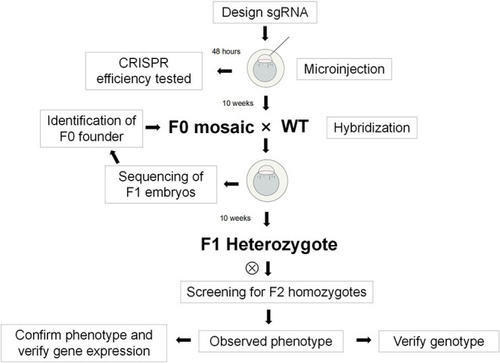
Flow chart of the experiment. |
|
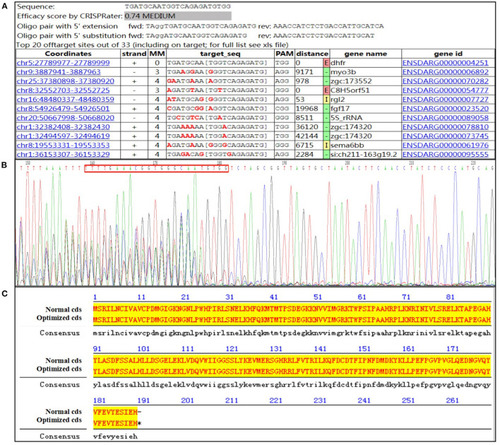
Design of guide RNA and identification primer. (A) Guide #5 TGATGCAATGGTCAGAGATGTGG; (B) the sequencing result of the activity verification; (C) the optimized amino acid sequence alignment (the lowercase font is the optimized base). |
|
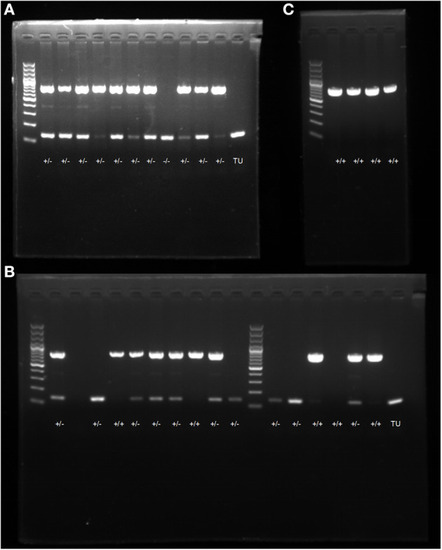
PCR electrophoresis diagram. (A) screening and genotype identification of F1 generation zebrafish; (B) identification of positive expressions of genotypes in zebrafish; (C) self-progeny genotype identification of F1 generation heterozygous zebrafish. |
|
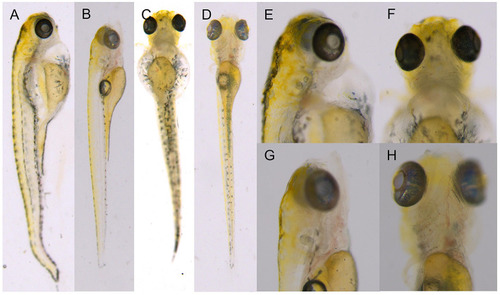
F2 generation zebrafish KI homozygotes at 6 dpf. (A,C,E,F) F1 heterozygous self-progeny. (B,D,G,H) self-progeny of TU. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
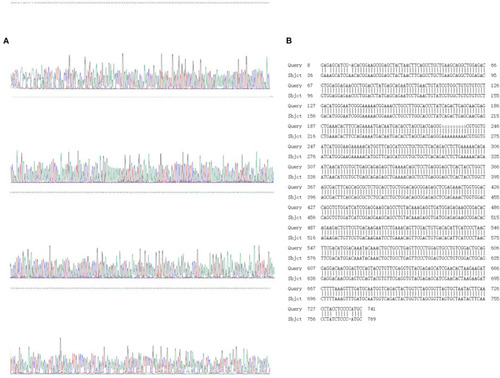
Sanger sequencing and sequence alignment analysis results. (A) Sanger sequencing results; (B) design sequence and sequencing alignment results. |
|
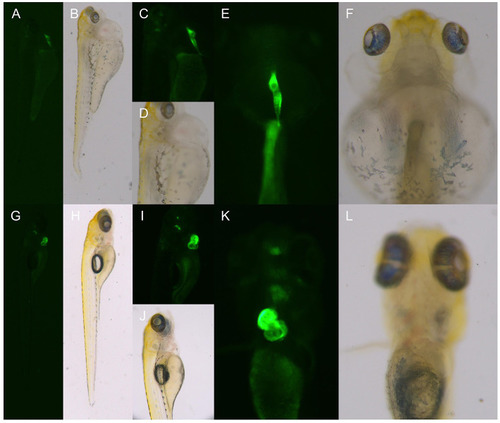
The phenotype of the hybrid offspring of the TgG fluorescent line. (A–F) TgG homozygous fluorescent strain dhfr. (G–L) TgG fluorescent strain TU. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
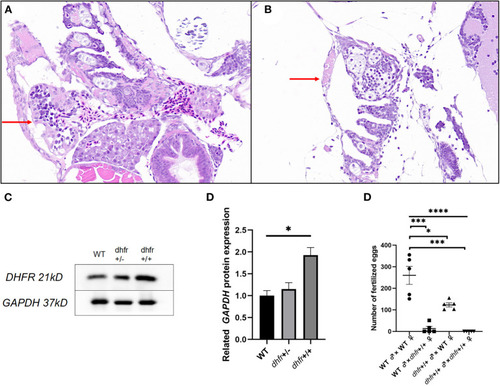
Results of pathology, western blot, and hybridization experiments. (A) TU zebrafish; (B) F1 dhfr heterozygous self-progeny (the red arrow points to the heart area). (C,D) WT, dhfr KI heterozygote, and dhfr KI homozygous DHFR protein expression analysis (GAPDH was used as an internal control). E: impaired fertility in zebrafish knocked in by dhfr (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). |