- Title
-
Deletion of lrrk2 causes early developmental abnormalities and age-dependent increase of monoamine catabolism in the zebrafish brain
- Authors
- Suzzi, S., Ahrendt, R., Hans, S., Semenova, S.A., Chekuru, A., Wirsching, P., Kroehne, V., Bilican, S., Sayed, S., Winkler, S., Spieß, S., Machate, A., Kaslin, J., Panula, P., Brand, M.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
(A) Alignment of the whole sequence and the individual domains of human LRRK2 (NP_940980) and zebrafish Lrrk2 (NP_001188385) proteins revealed a high degree of conservation of the catalytic core. The percentages of identity (same residues at the same positions in the alignment) and similarity (identical residues plus conservative substitutions) are indicated. Abbreviations: aa, amino acids; ANK, ankyrin domain; COR, C-terminal of Ras of complex proteins; LRR, leucine-rich repeat domain. (B) Scheme reproducing the EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
(A and B) Increased cell death in the brains of mzLrrk2 larvae (5 dpf) as revealed by TUNEL assay. Quantification was carried out over the whole brain, subdivided into anterior (telencephalon), middle (diencephalon, mesencephalon), and posterior (rhombencephalon) portions. (A) Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Plot represents means ± s.e.m. Statistical analyses: two-tailed Student’s |
|
(A) The zebrafish CA cell populations in the rostro-caudal axis from the olfactory bulb to the |
|
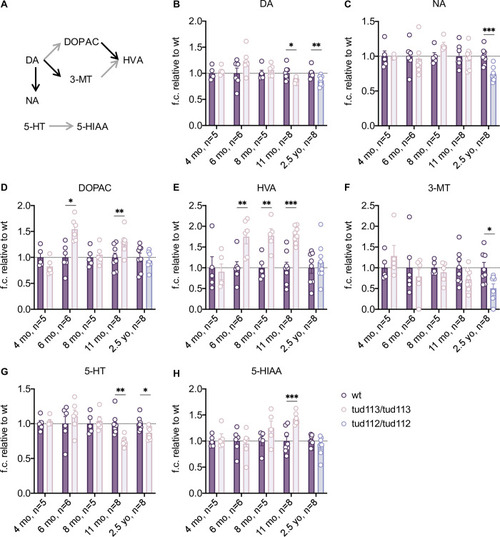
(A) Simplified scheme of the catabolism of dopamine and serotonin in the zebrafish brain. Each arrow represents a distinct enzymatically-catalyzed step. Grey arrows indicate the reactions catalyzed by the combined action of monoamine oxidase (MAO)/aldehyde dehydrogenase. Abbreviations: 3-MT, 3-methoxytyramine; 5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 5-HT, serotonin; DA, dopamine; DOPA, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid; HVA, homovanillic acid; NA, noradrenalin. (B-H) Levels of biogenic amines and their catabolites in the brain of adult maternal-zygotic PHENOTYPE:
|