- Title
-
Endogenous zebrafish proneural Cre drivers generated by CRISPR/Cas9 short homology directed targeted integration
- Authors
- Almeida, M.P., Welker, J.M., Siddiqui, S., Luiken, J., Ekker, S.C., Clark, K.J., Essner, J.J., McGrail, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
CRISPR/Cas9 short homology directed targeted integration strategy for efficient recovery of Cre knock-in alleles. ( |
|
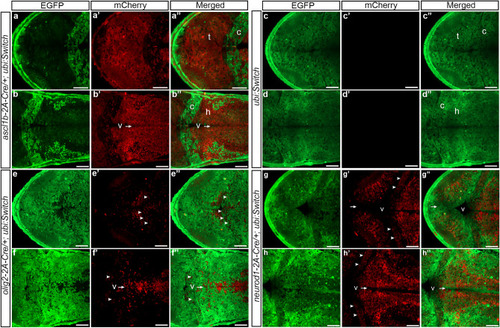
Expression of 2A-Cre integration alleles recapitulates |
|
Transgenic |
|
|
|
Tamoxifen regulated CreERT2 recombinase activity in F0 somatic targeted embryos. ( |