- Title
-
The Requirement of Sox2 for the Spinal Cord Motor Neuron Development of Zebrafish
- Authors
- Gong, J., Hu, S., Huang, Z., Hu, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, J., Qian, P., Wang, C., Sheng, J., Lu, X., Wei, G., Liu, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Mol. Neurosci.
|
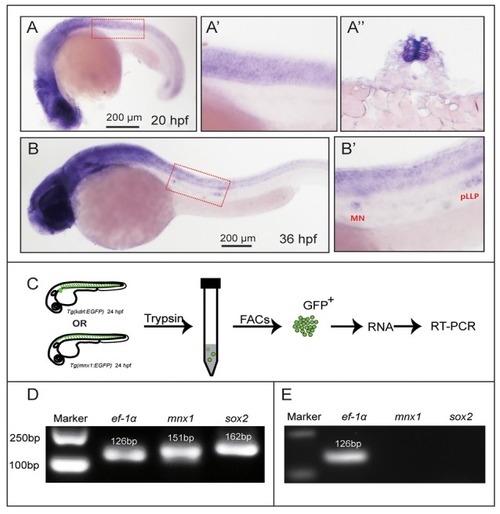
Sex-determining region Y box 2 (Sox2) expression analyses in the spinal cord and motor neurons. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Primary motor neuron morphogenesis defects in the Sox2 knockout zebrafish. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
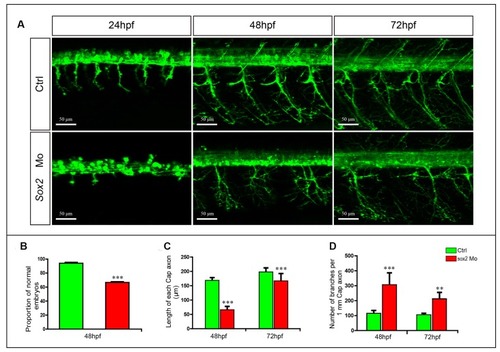
Primary motor neuron developmental defects in the Sox2 morphants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Sox2 deficiency suppressed neuronal cell differentiation. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
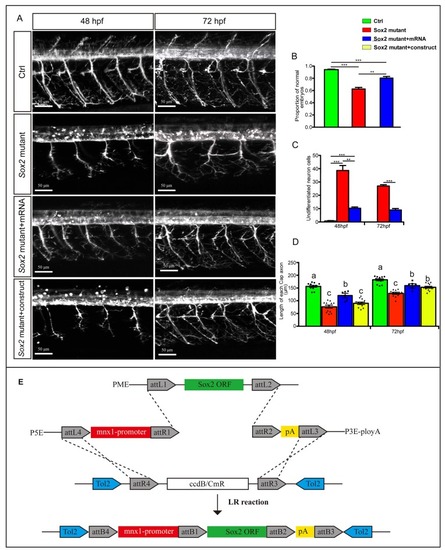
Overexpressions of Sox2 rescued the motor neuron defects in Sox2 mutant embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The results of transcriptomic profiling in Sox2 mutant and wild-type zebrafish. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|