- Title
-
Association of Rare Genetic Variants in Opioid Receptors with Tourette Syndrome
- Authors
- Depienne, C., Ciura, S., Trouillard, O., Bouteiller, D., Leitã O, E., Nava, C., Keren, B., Marie, Y., Guegan, J., Forlani, S., Brice, A., Anheim, M., Agid, Y., Krack, P., Damier, P., Viallet, F., Houeto, J.L., Durif, F., Vidailhet, M., Worbe, Y., Roze, E., Kabashi, E., Hartmann, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y)
|
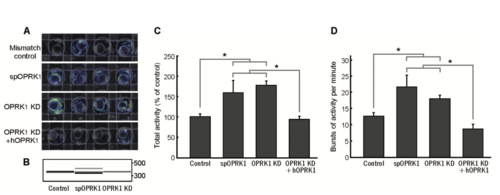
Knockdown of the Zebrafish OPRK1 Orthologue Results in Hyperactivity during Development. (A) Activity heatmap illustrating sponta- neous movement of 28 hpf embryos inside the chorion during a 10 seconds period. Higher levels of activity are evident in embryos injected with oprk1 splice-blocking AMO (spOPRK1) or ATG-targeting AMO (OPRK1 KD) when compared to mismatch AMO-injected embryos (Mismatch control). Expression of human OPRK1 transcript (hOPRK1) rescues the hyperactivity phenotype. (B) RT-PCR product of amplification of a region spanning exons 2 and 3 of the zebrafish oprk1 transcript. Injection of the splice-blocking AMO (spOPRK1) results in a defective splicing in this region. (C) Quantification of the total activity of 28 hpf zebrafish embryos. (D) Quantification of the frequency of movement bursts in the 28 hpf embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|