- Title
-
Targeted resequencing identifies genes with recurrent variation in cerebral palsy
- Authors
- van Eyk, C.L., Corbett, M.A., Frank, M.S.B., Webber, D.L., Newman, M., Berry, J.G., Harper, K., Haines, B.P., McMichael, G., Woenig, J.A., MacLennan, A.H., Gecz, J.
- Source
- Full text @ NPJ Genom Med
|
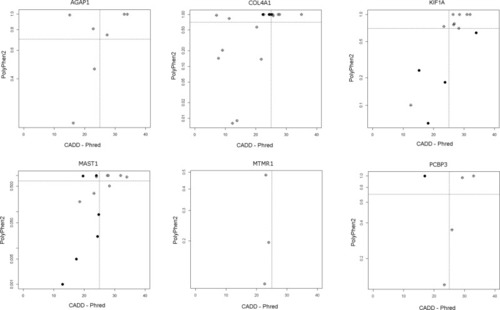
Scatterplots of CADD Phred vs PolyPhen2 scores for variants in genes with an overrepresentation of pathogenic variants in cerebral palsy cases compared to 1000 genomes controls. Controls—filled dots, CP cases—crossed dots |
|
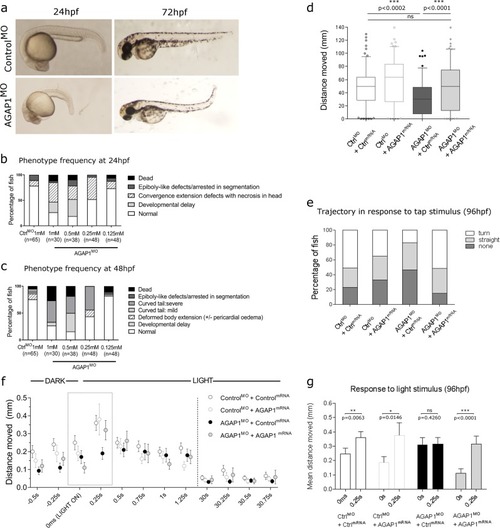
AGAP1 morphant zebrafish show gross developmental defects, neurological deficits and reduced motility. |