- Title
-
SETD5 Regulates Chromatin Methylation State and Preserves Global Transcriptional Fidelity during Brain Development and Neuronal Wiring
- Authors
- Sessa, A., Fagnocchi, L., Mastrototaro, G., Massimino, L., Zaghi, M., Indrigo, M., Cattaneo, S., Martini, D., Gabellini, C., Pucci, C., Fasciani, A., Belli, R., Taverna, S., Andreazzoli, M., Zippo, A., Broccoli, V.
- Source
- Full text @ Neuron
|
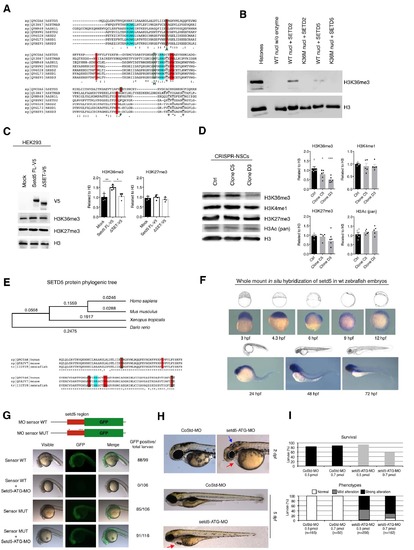
Additional evidences of SETD5 as H3K36 methyltransferase and zebrafish morfants’ characterization, related to Figure 8. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences of SETD5 and other H3K36 methylases (SETMAR, ASH1L, SETD2, NSD2, NSD1, NSD3). Residues important for catalytic activity (red) and S-adenosyl methionine binding (blue) and experimental mutations (green) are highlighted. (B) Nucleosome assay with either WT or K36M mutated nucleosomes for testing: no enzyme, recombinant SETD2 and short version of SETD5, revealed by Western blot. (C) Western blot for H3 methylations on protein lysates from overexpression experiment in HEK293 cells of either mock plasmid, or full-lenght version of SETD5 tagged with V5 with or without SET domain; right, quantification (shown as mean + s.e.m. with dots representing individual samples): H3K36me3, n = 3, mock vs SETD5 * p = 0.0251, SETD5 vs DSET * p = 0.0227; H3K27me3, n = 3, mock vs SETD5 p = 0.8035, SETD5 vs DSET p = 0.2106; all measurements statistically compared using unpaired t test. (D) Western blot for epigenetic marks on protein lysates from control NSCs and two clones of NSCs mutated in Setd5 by CRISPR/Cas9; right, quantification (shown as mean + s.e.m. with dots representing individual samples): n = 5, Ctrl vs C5 *** p = 0.0009, Ctrl vs D3 *** p = 0.0001; H3K36me3, n = 5, Ctrl vs C5 * p = 0.0324, Ctrl vs D3 *** p = 0.0005; H3K4me1, n = 5, Ctrl vs C5 p = 0.7360, Ctrl vs D3 p = 0.7302; H3K27me3, n = 5, Ctrl vs C5 p = 0.9587, Ctrl vs D3 * p = 0.0401; H3Ac, n = 5, Ctrl vs C5 p = 0.6815, Ctrl vs D3 p = 0.3939; all measurements statistically compared using two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E) (Top) phylogenic tree of human, mouse, Xenopus tropicalis and zebrafish SETD5 amino acid sequences (MEGA5 software); numbers represent amino acid differences per site. (Bottom) alignment of SET domain of zebrafish Setd5 protein and its human and mouse orthologues. The amino acids expected to play a key role in the catalytic activity of the protein as well as those mutated in for in vitro assay, as reported in A, are evidenced. (F) Whole mount in situ hybridization of setd5 mRNA on zebrafish embryos at different developmental stages. An antero-posterior expression gradient is evident starting from 24 hours post fertilization (hpf). (G) Validation of setd5 morpholino (setd5-ATG-MO) efficiency in zebrafish embryos injected with mRNA sensor containing the GPF encoding sequence carrying upstream the setd5-ATG-MO target sequence, either wild type (WT) or mutated (MUT). (H) Phenotypes of zebrafish larvae 2 and 5 days after fertilization (dpf) following injection of 0.5pmol setd5-ATG-MO or a control Standard morpholino (CoStd-MO). Microcephaly is highlighted by reduced eye size (circular dotted line); blue and red arrows point to brain edema and pericardial edema, respectively. (I) Survival rate at 24 hpf and phenotype quantitation of 48 hpf zebrafish larvae after injection of 0.5 or 0.7pmol of setd5-ATG-MO or CoStd-MO/embryo. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|