- Title
-
Calaxin is required for cilia-driven determination of vertebrate laterality
- Authors
- Sasaki, K., Shiba, K., Nakamura, A., Kawano, N., Satouh, Y., Yamaguchi, H., Morikawa, M., Shibata, D., Yanase, R., Jokura, K., Nomura, M., Miyado, M., Takada, S., Ueno, H., Nonaka, S., Baba, T., Ikawa, M., Kikkawa, M., Miyado, K., Inaba, K.
- Source
- Full text @ Commun Biol
|
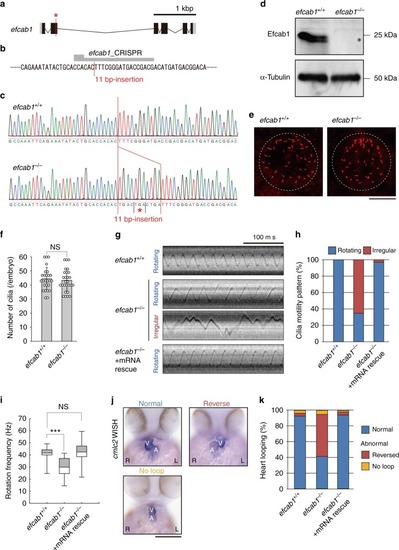
Mutation of zebrafish efcab1 causes abnormal motility of Kupffer’s vesicle cilia. a Genomic organization of zebrafish efcab1. Black boxes: exons. Gray boxes: untranslated regions. Red asterisk indicates the genome-editing target site. b CRISPR/Cas9 target sequence. c Sanger sequencing of efcab1+/+ and efcab1−/− fish around the genome-editing target site. The 11 bp-insertion in efcab1−/− includes a stop codon (red asterisk). d Immunoblot of testis lysate. The induced mutation deleted Efcab1 (asterisk). α-tubulin: loading control. e Kupffer’s vesicle cilia were visualized by immunofluorescence staining with acetylated-tubulin antibodies. f Measurement of the number of Kupffer’s vesicle cilia showed no significant differences between efcab1+/+ and efcab1−/− fish. N (embryo) = 26 (efcab1+/+) and 27 (efcab1−/−). Values indicate mean ± SD. g Typical kymographs of Kupffer’s vesicle cilia in efcab1+/+, efcab1−/−, and mRNA-rescued efcab1−/− fish. Kymograph patterns were categorized into two classes: rotating (blue) and irregular (red). h Ratios of each motility class. N (cilia) = 55 (efcab1+/+), 72 (efcab1−/−) and 65 (mRNA-rescued efcab1−/−). i Rotational frequencies of Kupffer’s vesicle cilia. Boxes correspond to the first and third quartiles, and whiskers extend to the full range of the data. N (cilia) = 55 (efcab1+/+), 25 (efcab1−/−) and 63 (mRNA-rescued efcab1−/−). ***p < 0.001 vs. efcab1+/+ (Student’s t-test). j Ventral views of 48 hpf embryos. Heart looping was visualized by whole-mount in situ hybridization of cmlc2. L, left; R, right; V, ventricle; A, atrium. k Directions of heart looping. N (embryo) = 108 (efcab1+/+), 114 (efcab1−/−), and 51 (mRNA-rescued efcab1−/−) PHENOTYPE:
|