- Title
-
Modeling GATAD1-Associated Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Adult Zebrafish.
- Authors
- Yang, J., Shah, S., Olson, T.M., Xu, X.
- Source
- Full text @ J Cardiovasc Dev Dis
|
Assessment of the cardiac expression of gatad1 in zebrafish. (A) The relative expression level of gatad1 in different tissues were revealed by real-time RT-PCR using 18s as internal control. Cardiac expression was defined as 1 and used as a reference. The brain has the highest gatad1 expression; (B) Different expression levels of gatad1 in embryonic and adult zebrafish hearts were revealed by RNA sequencing. gatad1 expression in the embryonic heart is higher than that in the adult heart; (C) Cardiac expression of gatad1 transcripts was also revealed by in situ hybridization in 2 dpf zebrafish embryos. RPKM: number of reads per kilobase per million reads. |
|
Subcellular localization of the Gatad1 protein in the embryonic zebrafish heart. After the myl7:gatad1-GFP construct was injected into 1-cell staged embryos, hearts from 2 dpf embryos were dissected for immunostaining and imaging. (A) Gatad1-GFP shows strong expression in nuclei and relatively weak expression in myofibrils, overlapping with Actin as revealed by phalloidin staining; (B) Gatad1-GFP partially overlaps with Z-discs marked by Actinin (arrows); (C) Gatad1-GFP forms alternatively striated patterns with M-line marked by Myomesin (arrowheads). * Nucleus; Scale bar 5 μm. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |
|
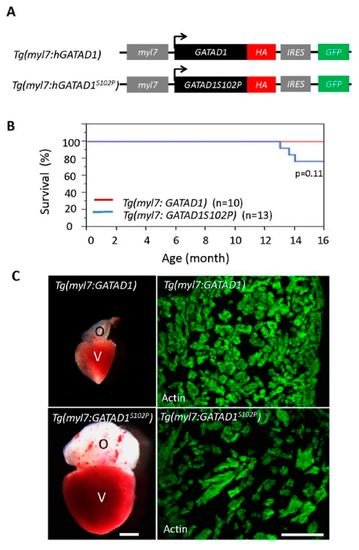
Generating and phenotyping GATAD1 transgenic fish. (A) Schematic illustration of constructs that were used to generate two transgenic fish lines expressing either human wild type GATAD1 or GATAD1-S102P mutation. The GATAD1 gene is flanked by the myl7 enhancer at its 5′ terminal to drive cardiomyocyte-specific expression, and it has an HA tag and IRES-EGFP at its 3′ terminal to facilitate detection of ectopic gene expression and fish propagation; (B) The transgenic fish expressing mutant GATAD1 started to die at approximately 12 months of age, and all transgenic fish expressing wild type GATAD1 were able to survive to 16 months; (C) Severe cardiac hypertrophy in a Tg(myl7:hGATAD1S102P) fish. Left panel, images of a heart dissected from a Tg(myl7:hGATAD) and a Tg(myl7:hGATAD1S102P) fish at 17 months of age, separately. The heart from this single Tg(myl7:hGATAD1S102P) fish exhibits significantly enlarged ventricle and out flow tract. Right panel, phalloidin staining revealed less dense myofibril and wider myofibril in the heart of this single Tg(myl7:hGATAD1S102P) fish. V, ventricle; O, out flow tract; Scale bar 0.5 mm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
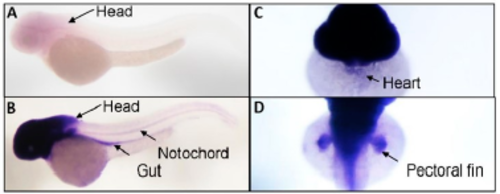
Figure S1. Tissue-specific expression of gatad1 transcripts was revealed by in situ hybridization in 2 dpf zebrafish embryos. Short-time stain only revealed head expression of gatad1 (A), but long time stain show gatad1 expression in gut, notochord, heart and pectoral fin (B–D). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|