- Title
-
Analysis of Zebrafish Larvae Skeletal Muscle Integrity with Evans Blue Dye
- Authors
- Smith, S.J., Horstick, E.J., Davidson, A.E., Dowling, J.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Vis. Exp.
|
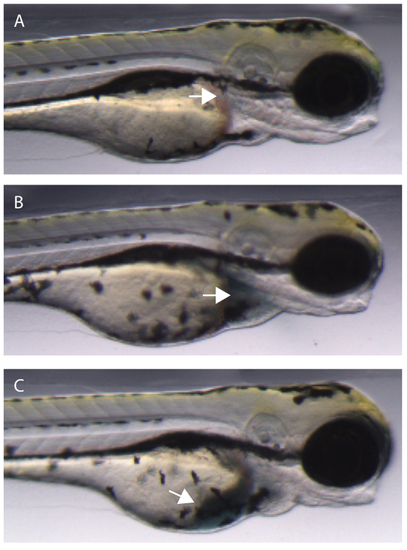
Injecting EBD injection mix into the common cardinal vein (CCV) of a zebrafish embryo. (A) Uninjected embryo. Arrow denotes ideal location for CCV injection. (B) Successful injection into the CCV. The dye enters the heart chambers (arrow) and begins to be pumped through the vasculature. (C) An unsuccessful CCV injection will result in some or all of the dye entering the yolk sac of the embryo (arrow). |
|
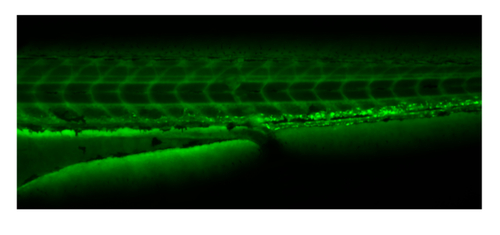
Embryos can be sorted for successful injection by observing FITC-dextran distribution under green fluorescence throughout the vasculature immediately following injection and prior to EBD uptake. |
|
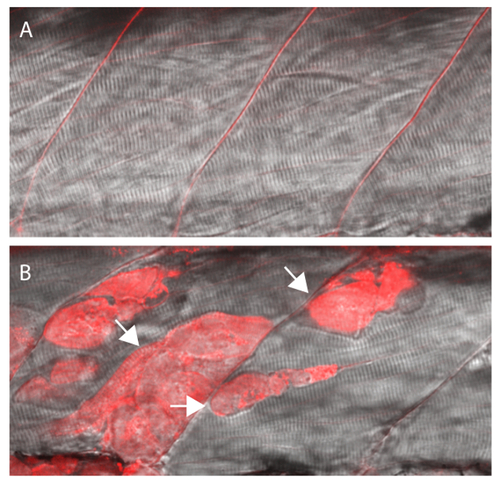
EBD will be taken up by fibers with damaged membranes. (A) Wildtype siblings showing no EBD fluorescence in muscle fibers. (B) Sapje homozygous mutant with EBD fluorescence within multiple muscle fibers (arrows). All larvae were injected with the EBD injection mix and analyzed after a 4 hr incubation period at 3 dpf. Siblings and mutants were sorted by muscle fiber detachment prior to CCV injection. PHENOTYPE:
|