- Title
-
Neuronal labeling patterns in the spinal cord of adult transgenic Zebrafish
- Authors
- Stil, A., Drapeau, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Neurobiol.
|
Distribution of pan-neuronal and glial markers HuC/D, NF, SV2, GFAP, and Olig2. Neurons are stained with anti-HuC/D antibody (A1-A3). The 3A10 antibody recognizes neurofilament (NF)-associated proteins and labels axonal tracts (B1-B3). The anti-SV2 (synaptic vesicle protein 2) is used to highlight synaptic terminals (C1-C3). Glial cells are identified with the zrf-1 antibody that recognizes glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, D1-D3). Oligodendrocytes are visualized in olig2:GFP transgenic fish (E1-E3). |
|
Labeling pattern of GFP in the spinal cord of adult isl1:GFP transgenic fish. In isl1:GFP larvae, transgene expression is mostly seen in secondary motoneurons (asterisk) and ventral roots (arrow, A). Transversal (B) and coronal (C) sections of adult spinal cord show large GFP-positive cell bodies in the dorsal part (white asterisks), and smaller cells more ventrally (magenta asterisks). Processes (arrow, B) extend in the upper region of ventral horns. The start of ventral roots (arrowheads, B) is stained. No signal is detected in the dorsal part. Higher magnification highlights large and smaller cells with two or more processes (D). |
|
Labeling pattern of GFP in the spinal cord of adult hb9:GFP transgenic fish. In hb9:GFP larvae, GFP is driven in motoneurons and some interneurons (asterisk, A), and ventral roots (arrow, A). In adults, GFP positive fibers lie both in dorsal and ventral horns (arrow, B), and in the white matter, surrounding dlf and vlf. Some ventral commissural tracts are labeled (arrowhead, B). Cell bodies are located in the medial and the lateral parts of the ventral horn (asterisks, B, C). In the caudal part of V8, there is a strong staining above the central canal (arrows; B, inset; C). At higher magnification, GFP positive neurons show two processes (arrowheads, D). |
|
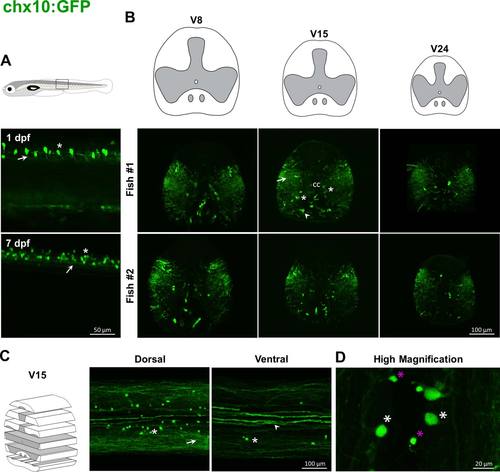
Labeling pattern of GFP in the spinal cord of adult chx10:GFP transgenic fish. In chx10:GFP embryos, GFP-positive cells are mostly glutamatergic interneurons (asterisk, A) with descending projections (arrow, A). In adults, dense projections are present throughout the gray and white matters (arrows, B, C) except in the more dorsal region. Cell bodies (asterisks, B, C) are located in medial and lateral parts of ventral horns. Some strongly labeled fibers are present in the white matter below the central canal (arrowheads, B, C). At higher magnification large cells stand out from smaller cells (respectively white and magenta asterisks, D). |
|
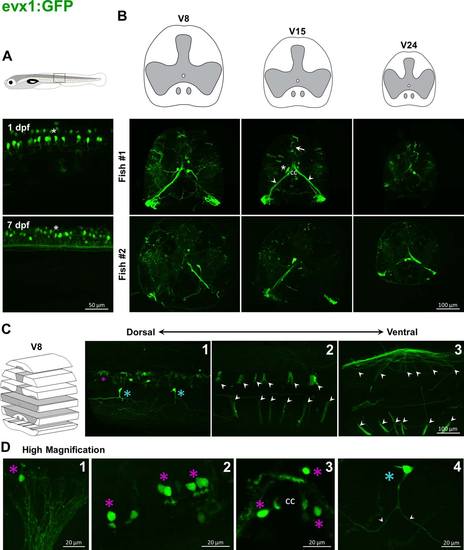
Labeling pattern of GFP in the spinal cord of adult evx1:GFP transgenic fish. In evx1:GFP embryos, GFP is driven in commissural interneurons (asterisk, A). In adults, cell bodies that project ventrally to the contralateral side along commissural paths are found adjacent to the central canal (asterisk, B). Some GFP-positive fibers sparsely covered sections (arrows, B, C). Some big bundles start above the central canal and go down to the ipsilateral ventral root (arrowheads, B, C), and their cell bodies are found around the central canal (magenta asterisks; C; D). Higher magnification shows other cells (blue asterisk, D) with processes extending to both rostral and caudal directions (arrowheads, D). |
|
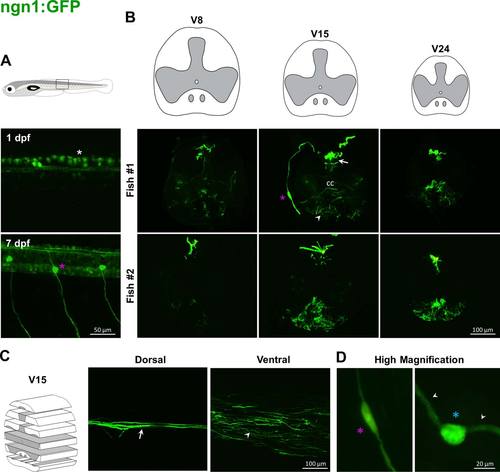
Labeling pattern of GFP in the spinal cord of adult ngn1:GFP transgenic fish. In ngn1:GFP embryos, the transgene is expressed in Rohon Beard sensory neurons (white asterisk, A, upper panel) and then in neurons of dorsal root ganglia (magenta asterisk, A, lower panel). In adults, GFP-positive fibers lie in dorsal horns (arrows, B, C). A cell body in the dorsal root ganglion and its axon reaching the dorsal horn is stained (magenta asterisks, B; D, left panel). Some processes are labeled at the level of the medioventral white matter (arrowheads, B, C). Higher magnification highlights rare large cells lying in dorsal horn (blue asterisk, D, right panel) with two processes (arrowheads, D, right panel). |
|
Characterization of cell identity in the spinal cord of adult GFP transgenic fish. Immunostaining with ChAT in isl1 (A) and hb9 (B) fish revealed GFP+/ChAT+ (arrows), GFP-/ChAT+ (arrowheads) and GFP+/ChAT- (open arrowheads) cells. C. The GFP-positive population in olig2:GFP fish starting close to the central canal and sending ipsilateral projection to the ventrolateral edge of the spinal cord (arrow, inset) do not express GFAP. D. The basal part of ipsilateral bundles expressing GFP in evx1:GFP fish show SV2 positive puncta (white puncta, arrow, inset). |