- Title
-
Zebrafish WNK Lysine Deficient Protein Kinase 1 (wnk1) Affects Angiogenesis Associated with VEGF Signaling
- Authors
- Lai, J.G., Tsai, S.M., Tu, H.C., Chen, W.C., Kou, F.J., Lu, J.W., Wang, H.D., Huang, C.L., Yuh, C.H.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Spatial and temporal expression patterns of wnk1a and wnk1b. (A) wnk1a and wnk1b mRNA expression profiles as determined by q-RT-PCR. At least three replicates were performed, and the average number of molecules was calculated using a standard curve from a q-RT-PCR assay. The standard deviations are shown in the graph. The red and blue lines indicate the wnk1a and wnk1b expression profiles, respectively. (B |
|
Statistical analysis of the length of intersegmental vessels in flk1, flt4, wnk1a, wnk1a 5MM, wnk1a upstream and wnk1b upstream morpholino-injected embryos. The effects of (A) flk1 MO, (B) flt4 MO, (C) wnk1a MO, (D) wnk1a 5 base mismatch MO, (E) wnk1a upstream MO, and (F) wnk1b upstream MO on the length of intersegmental vessels. Morpholino injection has a dose-dependent effect on intersegmental vessel formation and growth. All experiments were performed at least three times, and the average ISV length was calculated along with the standard deviation, which is labeled on each bar. Red indicates that the ISVs grew to full length, orange indicates that the ISVs were 75% of the normal length, yellow indicates 50%, green indicates 25%, and light blue indicates that no ISVs were observed in the embryos. The differences between treatments were assessed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. Significant differences between the morphants and controls are indicated (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; and ***, P<0.001). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
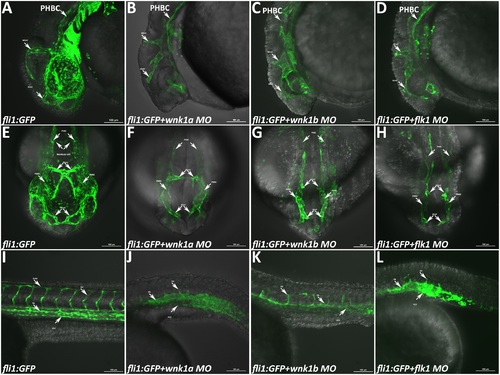
Phenotype of Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected with various morpholinos and imaged with a confocal microscope. (A-D) Lateral views of the heads of uninjected control embryos and wnk1a, wnk1b and flk1 morphants at 33 hpf. (E-H) Frontal views of the heads of uninjected control embryos and wnk1a, wnk1b and flk1 morphants at 33 hpf. (I-L) Lateral views of the trunk in uninjected control embryos and wnk1a, wnk1b and flk1 morphants at 33 hpf. Important vessels are indicated with arrows and labeled, with the full name given in the text. Scale bar: 100 µm. |
|
Effect of wnk1a or wnk1b knockdown on vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos. (A, B) Whole mount in situ hybridization for etv2 at 14 and 18 hpf in uninjected control embryos (A1, B1), wnk1a morphants (A2, B2), and wnk1b morphants (A3, B3). Flat mounts of de-yolked embryos were prepared. (C) GFP fluorescence was used to assay ISV formation in uninjected control embryos (C1), wnk1a morphants (C2), and wnk1b morphants (C3) at 33 hpf. (D1) etv2 expression in uninjected control, wnk1a and wnk1b morphants as a percentage of embryos exhibit strong or expression, (D2) ISV length in wnk1a and wnk1b morphants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Effect of knockdown of the PI3K ortholog on ISVs and the rescue effects of wild-type wnk1a, wnk1a containing an Akt phosphorylation site mutation and kinase-deficient wnk1a on flk1 morphants. (A) The effects of pi3kc2α MO on the length of intersegmental vessels. (B) Two Thr35 mutations and one Lys206 mutation were generated using site-directed mutagenesis. The sequence of wild-type wnk1a aligned with Thr35 and Lys206 mutants, which are Akt phosphorylation site and kinase domain mutants, respectively. (C) Co-injection of wnk1a mRNA rescues flk1 morphants. Quantitative analysis of the length of the ISVs in flk1 morphants co-injected with various wnk1a mRNAs. Experiments were performed at least three times, and the number of embryos analyzed is shown in the bar graph. Red indicates that the ISVs grew to full length, orange indicates that the ISVs were 75% of the normal length, yellow indicates 50%, green indicates 25%, and light blue indicates no ISVs were observed in the embryos. The differences between treatments were assessed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. Significant differences between the morphants and controls are indicated (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; and ***, P<0.001). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
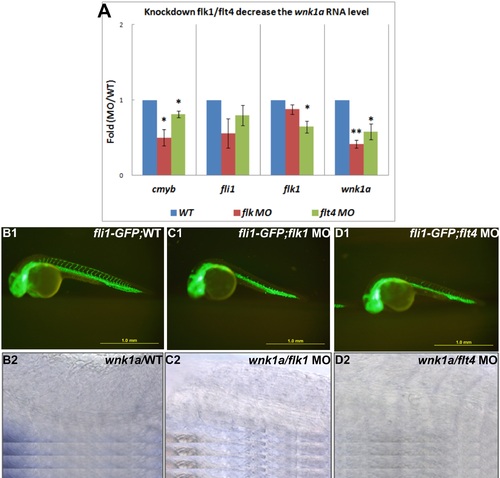
Injections of flk1 MO and flt4 MO decrease wnk1 mRNA expression. (A) Relative fold-change comparisons between flk1 and flt4 morphants and uninjected controls. Comparison of mRNA expression levels at 33 hpf for important transcription factors, receptors, and wnk1. Blue, red, and green bars denote mRNA expression in wild-type embryos, flk1 morphants and flt4 morphants, respectively. The x-axis indicates the expressed genes, and the y-axis shows the fold differences between the morphants and the control. The differences between treatments were assessed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. Significant differences between the morphants and the controls are indicated (*, P<0.05 and**, P<0.01). (B1, C1, D1) The ISVs are affected in morphants compared with wild-type embryos. (B2, C2 and D2) The expression of wnk1a is reduced in the PCV in flk1 and flt4 morphants. wnk1a mRNA was detected with in situ hybridization in wild-type embryos (B2), flk1 morphants (C2) and flt4 morphants (D2). |
|
Temporal expression patterns of wnk1a and wnk1b. Whole mount in situ hybridization to detect wnk1a (A1 |