- Title
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition as a pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson disease
- Authors
- Fitzmaurice, A.G., Rhodes, S.L., Lulla, A., Murphy, N.P., Lam, H.A., O'Donnell, K.C., Barnhill, L., Casida, J.E., Cockburn, M., Sagasti, A., Stahl, M.C., Maidment, N.T., Ritz, B., and Bronstein, J.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
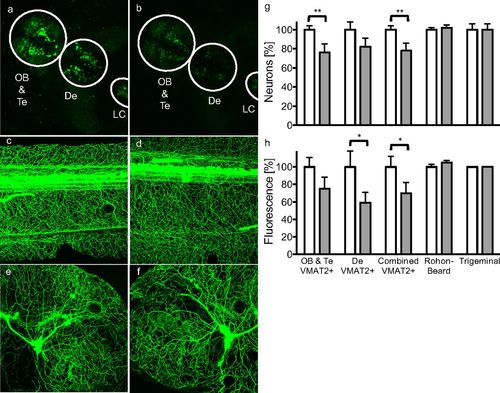
Aminergic neuronal damage in Danio rerio embryos exposed to benomyl. Representative confocal images of zebrafish embryos (A, C, and E) unexposed or (B, D, and F) bathed in 1 μM benomyl from 5 h until 120 h postfertilization are shown. (G) Neuronal counts (A and B) decreased in VMAT2+ anterior and diencephalic clusters of ETvmat2:GFP zebrafish exposed to benomyl (solid bars) but were unaffected in (C and D) Rohon-Beard and (E and F) trigeminal neurons in Tg(isl1[ss]:Gal4-VP16,UAS:EGFP)zf154 zebrafish. (H) Measurement of total fluorescence yielded similar results. Data are expressed as percent relative to vehicle controls (0.01% DMSO). *P < 0.1, **P < 0.05. De, diencephalon; LC, locus coeruleus; OB, olfactory bulb; Te, telencephalon. |