- Title
-
An mnr2b/hlxb9lb enhancer trap line that labels spinal and abducens motor neurons in zebrafish
- Authors
- Asakawa, K., Higashijima, S.I., and Kawakami, K.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
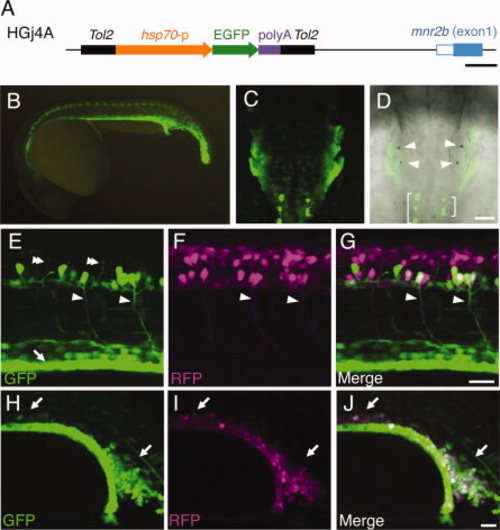
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression directed by the HGj4A insertion. A: Structure of the HGj4A insertion. The enhancer trap construct T2KHG (Nagayoshi et al., 2008) is composed of the Tol2 sequences (black), the zebrafish hsp70 promoter (orange), the GFP gene (green) and the SV40 polyA signal (purple). The 52 untranslated region and the first coding exon of the mnr2b gene are shown as the open and filled blue boxes, respectively. B: The lateral view of the HGj4A embryo at 22 hours postfertilization (hpf). C,D: The dorsal view of the HGj4A embryo at the hindbrain level at 22 hpf. The anterior is to the top. The GFP signal in C was merged into the bright field image in D. The arrowheads indicate the position of the otoliths. The brackets indicate the GFP-positive neuronal cells in the central nervous system. E–G: The lateral view of the trunk in the HGj4A;SAIGFF213A;UAS:RFP triple transgenic embryo at 22 hpf. The arrowheads indicate the CaP axons. The double arrowheads indicate the MiP axons. The arrow indicates the GFP expression in endodermal cells. H–J: The lateral view of the trunk in the HGj4A;Tg(gata1-RFP) double transgenic embryo at 22 hpf. The arrows indicate the intermediate cell mass, where the GFP and red fluorescent protein (RFP) signals are extensively overlapped. UAS, upstream activating sequence. Scale bars = 500 bp in A, 50 μm in C,D, 30 μm in E–J. |
|
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in the HGj4A embryos and larvae. A,B: The lateral view of the HGj4A embryo at 48 hpf (A) and larva at 120 hours postfertilization (hpf; B). C,D: The lateral view of the spinal cord in HGj4A embryo at 48 hpf (C) and larva at 120 hpf (D). The arrowheads and double arrowheads indicate the motor axons extending ventrally and dorsally, respectively. E,F: The single section the spinal cord of the HGj4A;Tg(vglut2a: loxPDsRed-GFP) double transgenic embryo at 48 hpf. In E, the GFP signal was merged with the red fluorescent protein (RFP) signal (vlut2, F). G,H: The single section of the spinal cord of HGj4A embryo at 48 hpf, stained with anti-Pax-2 antibody (magenta). In G, the GFP signal was merged with the Pax-2 signal (magenta, H). Scale bars = 50 μm in C,D, 30 μm in E–H. |
|
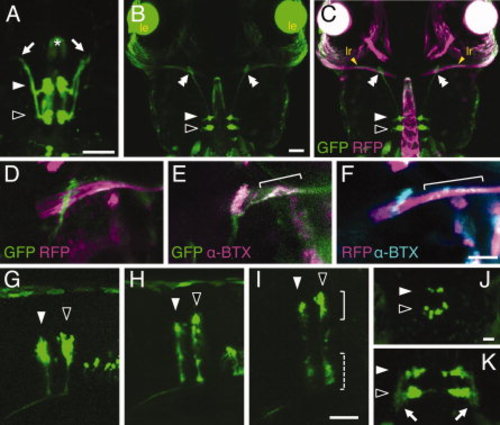
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in the hindbrain in the HGj4A larvae. A: Dorsal view of the hindbrain in the HGj4A embryo at 48 hours postfertilization (hpf). The arrows indicate the tip of the axon-like processes. The asterisk indicates the GFP signal in the notochord. The anterior is to the top. B,C: Dorsal view of the head region of the HGj4A;hspGFFDMC131B;UAS:RFP larvae at 72 hpf. The GFP signal (green) in B was merged into the red fluorescent protein (RFP) signal (magenta) in C. The bilateral saturated spheres are lens (le, in B). The green striations below the lens are autofluorescence generated from the pigment cells. In C, the yellow arrows indicate the lateral rectus muscles (lr). The double arrowheads indicate the position where the contact between the axons of the abducens motor neuron and the lateral rectus muscle is evident. The anterior is to the top. D–F: The dorsal view of the right lateral rectus muscles innervated by the abducens motor neurons at 120 hpf. D: An HGj4A;hspGFFDMC131B;UAS:RFP larva. E: An HGj4A larva stained with anti-GFP antibody (green) and α-Bungarotoxin (magenta). F: An hspGFFDMC131B larva stained with anti-RFP antibody (magenta) and α-Bungarotoxin (cyan). The brackets in E and F indicate the punctate AChRs. The anterior is to the top. G–I: The lateral view of the hindbrain at 48 hpf (G), 72 hpf (H), and 120 hpf (I). The brackets and dashed brackets indicate the dorsal and ventral GFP-positive clusters, respectively. J,K: Dorsal views of the hindbrain. The z-stacks of the dorsal (the bracket in I) and ventral (the dashed bracket in I) clusters are shown in J and K, respectively. The arrows indicate the dendritic structure. The anterior is to the top. In all panels, the filled and open arrows indicate the positions of the GFP-positive clusters, which correspond to r5 and r6, respectively. Scale bars = 50 μm in A–F, 20 μm in J,K |
|
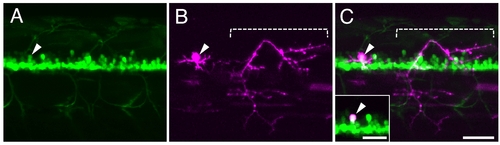
Single-cell labeling of the spinal motor neuron in HGj4A larvae. A–C: The lateral view of the trunk region of the HGj4A larvae injected with the mnx1/hlxb9:mCherry plasmid. The arrowhead indicates the soma of a GFP-positive cell expressing RFP that locates slightly dorsal to the densely aligned GFP-positive cells in the ventral spinal cord. The dashed bracket indicates the motor axon innervating the skeletal muscles. In C, the GFP signal (A) and was merged into the RFP (B) signal. The inset in C shows the image of the same larvae taken with a shorter exposure time for RFP and indicates the single GFP-positive cell (arrowhead) is expressing RFP. Scale bars = 50 μm in A–C, 30 μm in the inset. |
|
Transient expression of Gal4FF from the cis-regulatory element of the glyt2 gene in HGj4A;UAS:RFP larvae. A–C: The lateral view of the spinal cord of the HGj4A;UAS:RFP larvae injected with the glyt:GFF BAC construct at 48 hpf. The arrowheads indicate the somata of RFP-positive cells. In C, the RFP signal (A) and was merged into the GFP (B) signal. D: In total, 58 RFP-positive cells from five larvae were examined and, of these, two cells were GFP-positive. Scale bar = 30 μm in A–C. |