- Title
-
Anti-Mullerian hormone and 11 beta-hydroxylase show reciprocal expression to that of aromatase in the transforming gonad of zebrafish males
- Authors
- Wang, X.G., and Orban, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
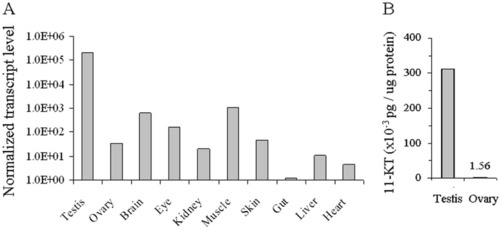
Analysis of the expression of cyp11b and the level of its product in the organs of adult zebrafish. A: Normalized transcript levels of cyp11b in 10 different organs of adult zebrafish as determined by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. B: The level of 11-KT, the main product of cyp11b in the testis, is two magnitudes higher than in the ovary. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
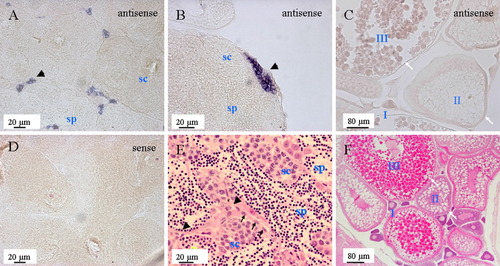
Analysis of cyp11b expression in the adult gonads by in situ hybridization. A: The expression of cyp11b is restricted to presumptive Leydig cells usually found in small clusters among big clusters of spermatocytes. B: Large clusters of presumptive Leydig cells could be found on the edge of the testis. C:cyp11b could not be detected in the ovary. D: Sense probe hybridization on adult testis, showing no nonspecific binding. E,F: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of adult testis and ovary. Black arrowhead, presumptive Leydig cells; black arrow, presumptive Sertoli cells; sc, spermatocytes; sp, spermatid. I, II, and III, stages of oocyte; white arrow, the position of granulosa cells and theca cells. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
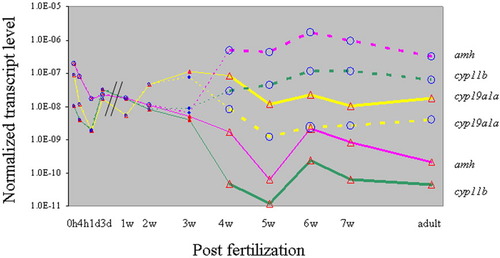
The comparative analysis of expression levels of amh, cyp19a1a and cyp11b during zebrafish development. Dashed lines, 0-2 weeks postfertilization (wpf) individuals; filled circles, 3 wpf enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) -negative individuals; filled triangles, 3 wpf EGFP-positive individuals; open circles, testes (4 wpf to adult) from EGFP-negative individuals; open triangles, ovaries (4 wpf to adult) from EGFP-positive individuals. For each data point, total RNAs from at least three individuals were pooled. RNAs of 0-3 days postfertilization (dpf) were collected from whole embryos, those of 1-3 wpf from body trunk containing gonads, and those of 3 wpf onward from isolated gonads. Data points located to the left of the parallel lines are from pooled embryos. Data from body trunks have been normalized with an experimental factor obtained by dividing the gene expression level in isolated gonads by the expression level in body trunk from the same set of EGFP-positive individuals of 3 wpf of age. All data were then normalized by β-actin levels. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
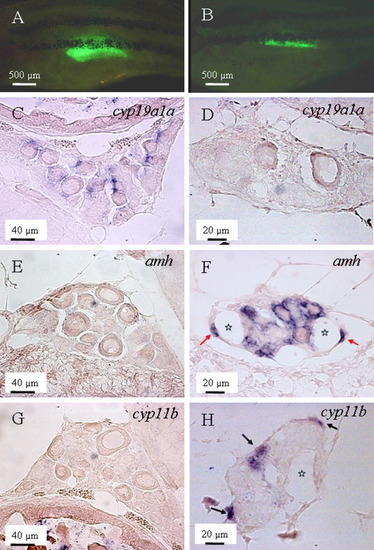
Expression pattern of cyp19a1a, amh, and cyp11b in the "normal" ovaries and transforming ovaries. A,C,E,G: The gonad of a female individual at 4 weeks postfertilization (wpf) of age is shown. B,D,F,H: The transforming gonad of a male individuals at 5 wpf of age is shown. A: An individual with "normal" ovary indicated by continuous accumulation of EGFP during the previous week. B: An individual with transforming ovary indicated by continuous decrease of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) during the previous week. C,D:cyp19a1a was expressed in the presumptive granulosa cells surrounding the normal oocytes (C), but not in the transforming ovary (D). E,F:amh initially could not be detected in the normal ovary (E), but became highly expressed in the cells surrounding the degenerating oocytes (F), and remained so even after the complete degeneration of oocytes (F, red arrow). G,H: Similarly to amh, cyp11b was also expressed during gonadal transformation. H: However, it was usually first expressed on the edge of the gonad (black arrows), without obvious correlation with the position of degenerating oocytes. Stars indicate the cavities after degeneration of oocytes. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
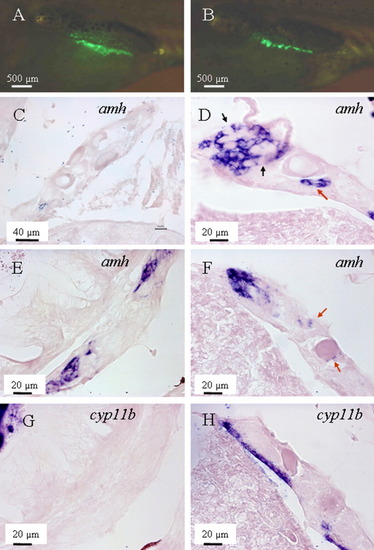
amh was expressed earlier than cyp11b during gonadal transformation. A, C, E, G: A male zebrafish at the early stage of transformation (35 days postfertilization [dpf]). B, D, F, H: Another male of the same age at advanced stage of gonad transformation. A,B: In vivo recording of enhanced green-fluorescent protein (EGFP) level in the gonad. C,E: In the early transforming gonads, amh could not be detected in the gonadal regions full of oocytes (C), but became detectable when the number of oocytes decreased (E). G: At the same time, cyp11b could not be detected anywhere during that time period. D,F: In the gonads at advanced stages of transformation, amh was expressed in most regions analyzed, localized to the somatic cells surrounding new germ cells (likely spermatogonia; black arrows on D) or close to the degenerating oocytes (red arrows on D and F). H:cyp11b only started to be expressed in some regions of the same gonad. It was expressed first on the edge of the gonads, then later also within the gonads (not shown). Notes: (1) due to variability of the transformation process male individuals of the same age might be at different stages of their gonad development; (2) sections shown on E and G were adjacent, and so were those on F and H. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|