- Title
-
Fgf3 and Fgf8 dependent and independent transcription factors are required for otic placode specification
- Authors
- Liu, D., Chu, H., Maves, L., Yan, Y.-L., Morcos, P.A., Postlethwait, J.H., and Westerfield, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
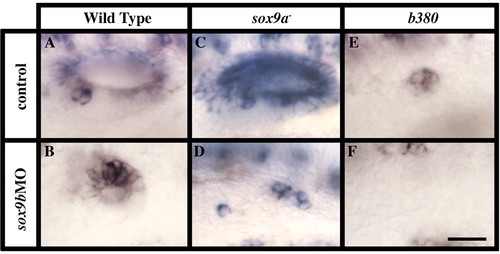
sox9b functions in otic specification. (A,B) The splice-blocking morpholino against sox9b (sox9bMO) significantly reduces the size of the otic vesicle (B, n=40 embryos), compared with that of wild-type control embryos (A). (C,D) In jellyfish (jef) mutants that harbor a retroviral insertion in the sox9a gene (jefhil134) (Amsterdam et al., 1999; Yan et al., 2002), injecting sox9b-MOs results in the loss of a morphologically recognizable otic vesicle (n=9 embryos), although a few dispersed pax2a-positive cells persist (D). In uninjected jef (sox9a) mutants (C, n=6 embryos), otic vesicles are slightly smaller than in wild-type control embryos (A). (E,F) Injecting sox9b-MO blocks formation of the residual otic cells of Dfb380 (4/6 Dfb380 embryos had residual pax2a-expressing cells, only 2/12 Dfb380 embryos had residual otic cells after injection with sox9b-MO). (A,B,E,F) prim-12 (28 h); (D,F) prim 25 (36 h). Side views, anterior towards the left, dorsal towards the top. Scale bar: 25 μm. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|